Top 15 Best Medical Devices and Equipment In India 2023
Medical Devices and Equipment in India

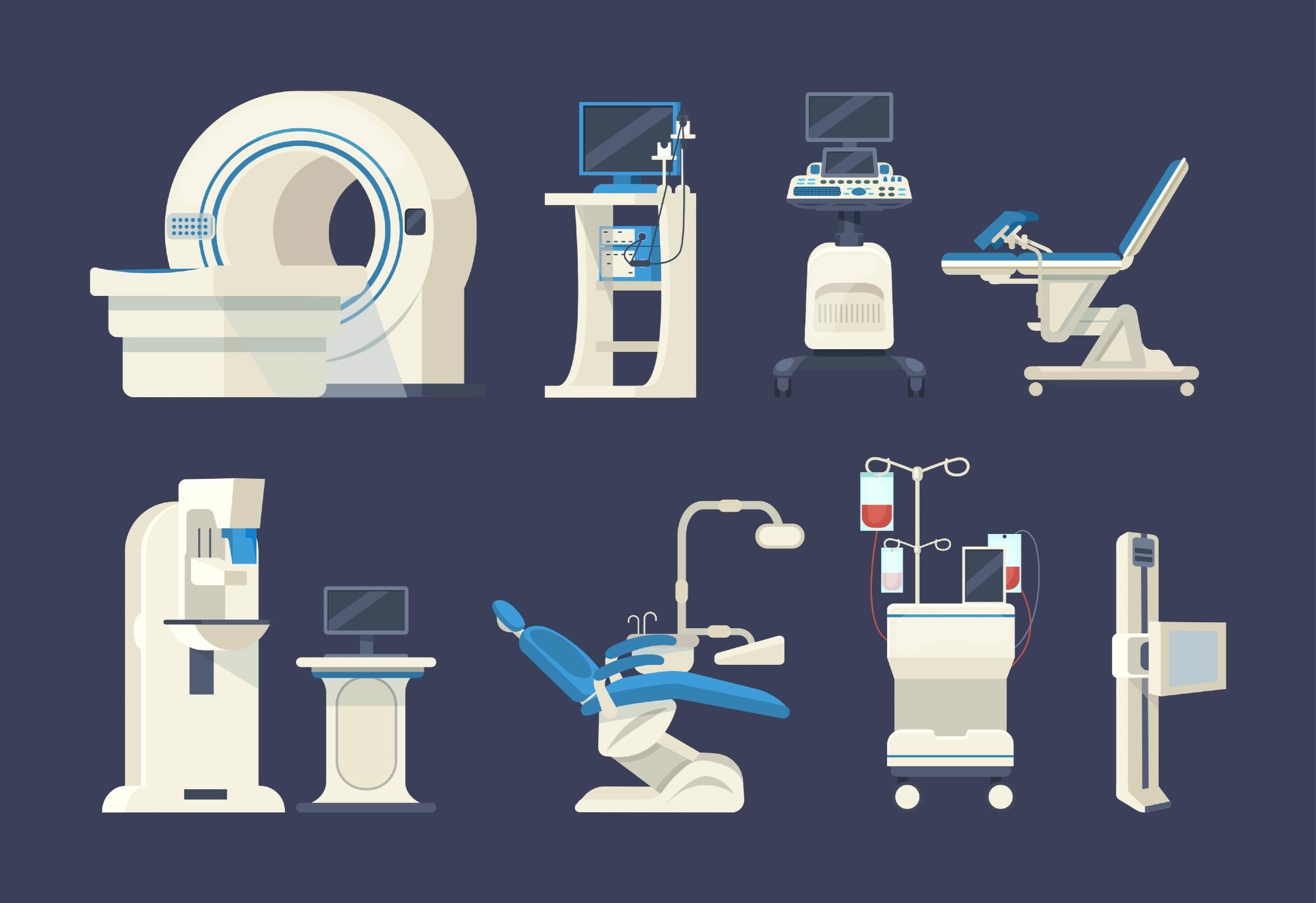
Medical devices and equipment refer to a broad range of tools, instruments, machines, and devices that are used by healthcare professionals to diagnose, treat, or prevent diseases, injuries, or other medical conditions. These devices can be as simple as a stethoscope or as complex as a robotic surgical system.
Medical devices and equipment can be classified into various categories based on their function and level of invasiveness. Some common examples include:
- Diagnostic devices: These devices are used to diagnose medical conditions and include tools like X-ray machines, CT scanners, and blood glucose monitors.
- Therapeutic devices: These devices are used to treat medical conditions and include tools like pacemakers, insulin pumps, and nebulizers.
- Surgical devices: These devices are used during surgical procedures and include tools like scalpels, forceps, and retractors.
- Monitoring devices: These devices are used to monitor patients’ vital signs and include tools like blood pressure monitors, heart rate monitors, and pulse oximeters.
Medical devices and equipment play a crucial role in modern healthcare, enabling healthcare professionals to provide better and more effective care to patients. These devices are subject to strict regulations to ensure their safety and efficacy, and they must undergo rigorous testing and approval processes before they can be used in clinical settings.
List of some of the most commonly used medical devices and equipment in India:
- Ultrasound machines
Ultrasound machines consist of a transducer, which emits sound waves and receives the echoes that bounce back from the body, and a computer that processes the data to create images. The images produced by ultrasound machines can be used to examine a wide range of organs and tissues, including the heart, liver, kidneys, and reproductive organs.
Some of the common applications of ultrasound machines include:
- Obstetrics and gynecology: Ultrasound machines are frequently used to monitor fetal development during pregnancy and to diagnose conditions such as ovarian cysts and uterine fibroids.
- Cardiology: Ultrasound machines are used to evaluate the heart’s structure and function and to diagnose conditions such as heart valve abnormalities and congenital heart defects.
- Abdominal imaging: Ultrasound machines are used to examine the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and other abdominal organs to diagnose conditions such as liver disease and pancreatic cancer.
- Musculoskeletal imaging: Ultrasound machines are used to diagnose conditions such as tendonitis, arthritis, and other musculoskeletal disorders.
- ECG machines
ECG machines work by detecting the electrical signals that are generated by the heart’s contraction and relaxation. The machine consists of electrodes, which are placed on the patient’s chest, arms, and legs, and a computer that records and analyzes the signals. The resulting ECG waveform can be used to assess the heart’s rhythm, rate, and conduction system.
Some of the common applications of ECG machines include:
- Diagnosing heart conditions: ECG machines are used to diagnose a wide range of heart conditions, such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and myocardial infarction.
- Monitoring cardiac health: ECG machines can be used to monitor patients with existing heart conditions to assess the effectiveness of treatments and to detect changes in heart function over time.
- Evaluating risk for heart disease: ECG machines can be used as part of routine physical exams to evaluate a patient’s risk for developing heart disease.
- Defibrillators
Defibrillators are medical devices used to treat life-threatening conditions such as cardiac arrest, where the heart stops beating or beats in an irregular pattern. Defibrillators deliver an electric shock to the heart, which can help restore normal heart rhythm and save the patient’s life.
There are two main types of defibrillators: external and internal. External defibrillators are used outside the body, and include manual defibrillators, automated external defibrillators (AEDs), and wearable cardioverter defibrillators (WCDs). Internal defibrillators are surgically implanted devices that deliver shocks directly to the heart.

Some of the common applications of defibrillators include:
- Cardiac arrest: Defibrillators are used to treat patients experiencing sudden cardiac arrest, where the heart stops beating or beats in an irregular pattern.
- Arrhythmias: Defibrillators can also be used to treat arrhythmias, which are abnormal heart rhythms that can be life-threatening.
- Heart failure: In some cases, defibrillators can be used as part of a treatment plan for patients with heart failure, a condition where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
- Oxygen concentrators
Oxygen concentrators are medical devices that concentrate oxygen from ambient air and deliver it to patients with respiratory conditions who require supplemental oxygen. They are used in healthcare settings and also in home care settings to help patients with conditions such as COPD, asthma, and other respiratory diseases.
Oxygen concentrators work by filtering out nitrogen and other gases from ambient air, leaving behind highly concentrated oxygen. The device then delivers the concentrated oxygen through a nasal cannula or mask to the patient.
Some of the common applications of oxygen concentrators include:
- COPD: Oxygen concentrators are commonly used to treat patients with COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), a chronic lung disease that makes it difficult to breathe.
- Asthma: Oxygen concentrators can also be used to treat patients with severe asthma, a condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways.
- Sleep apnea: Oxygen concentrators are sometimes used to treat patients with sleep apnea, a condition that causes breathing to stop and start during sleep.
- Ventilators
Ventilators are medical devices that support or replace the natural breathing process of patients who are unable to breathe on their own due to illness or injury. They are commonly used in hospitals, intensive care units (ICUs), and other healthcare settings to provide mechanical ventilation to patients who require respiratory assistance.
Ventilators work by delivering air to the patient’s lungs through a breathing tube that is inserted into the mouth, nose, or trachea. The machine delivers a predetermined amount of oxygen and air at a controlled rate and volume to assist with breathing. Some ventilators also have settings for controlling the timing and pressure of the air delivered to the patient.
Some of the common applications of ventilators include:
- Respiratory failure: Ventilators are used to treat patients with respiratory failure, a condition where the lungs are unable to deliver enough oxygen to the body.
- Trauma: Ventilators can also be used to treat patients who have suffered from trauma, such as spinal cord injuries or head injuries, that affect their ability to breathe on their own.
- Surgery: Ventilators are commonly used during surgical procedures that require general anesthesia, which can temporarily depress the respiratory system.
- Infusion pumps
Infusion pumps are medical devices that deliver fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into a patient’s bloodstream. They are commonly used in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings to deliver intravenous (IV) therapy to patients who require precise and controlled doses of medication or fluids.
Infusion pumps work by delivering fluids or medications through a sterile tubing system that is connected to the patient’s vein through a catheter or needle. The pump controls the flow rate, volume, and dosage of the medication or fluid being delivered, ensuring accurate and consistent administration.
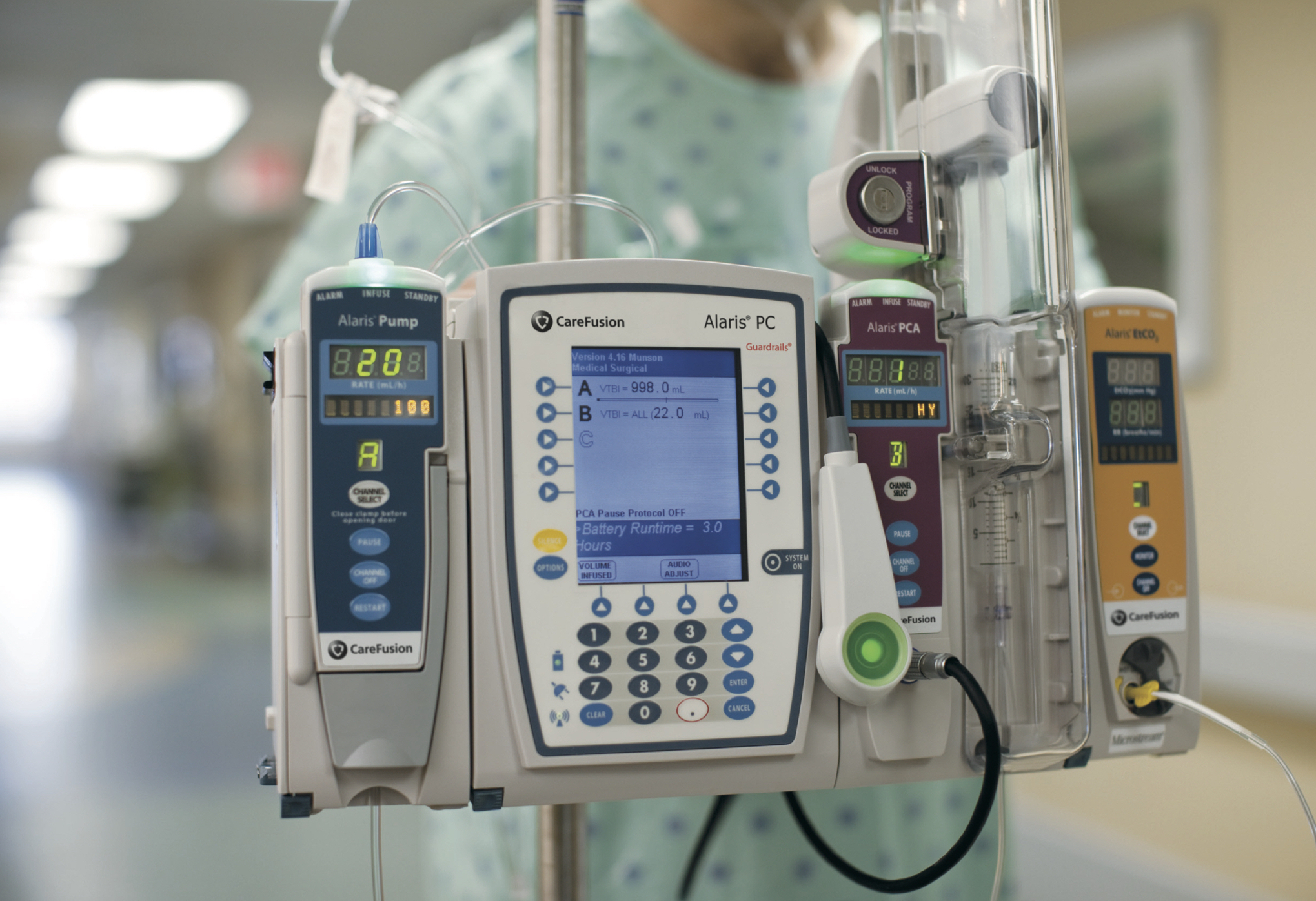
Some of the common applications of infusion pumps include:
- Pain management: Infusion pumps are commonly used to deliver pain medication to patients who require continuous pain relief.
- Chemotherapy: Infusion pumps can also be used to deliver chemotherapy drugs to cancer patients.
- Nutrition: Infusion pumps are used to deliver parenteral nutrition, which is a method of providing nutrients to patients who are unable to eat or digest food through the digestive system.
- Blood glucose monitors
Blood glucose monitors are medical devices that measure the level of glucose (sugar) in a person’s blood. They are commonly used by people with diabetes to monitor their blood glucose levels at home, and by healthcare professionals to diagnose and manage diabetes in patients.
Blood glucose monitors work by using a small lancet to prick the skin and draw a small drop of blood. The blood is then placed on a test strip, which is inserted into the monitor. The monitor then analyzes the blood and displays the glucose level on a digital screen.
Some of the common applications of blood glucose monitors include:
- Diabetes management: Blood glucose monitors are essential for people with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and adjust their treatment accordingly.
- Diagnosis of diabetes: Blood glucose monitors are also used by healthcare professionals to diagnose diabetes in patients who are at risk or have symptoms of the condition.
- Gestational diabetes: Blood glucose monitors can also be used by pregnant women with gestational diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels and ensure the health of the fetus.
- Blood pressure monitors
Blood pressure monitors are medical devices used to measure the force of blood against the walls of arteries as it flows through them. They are commonly used by healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor high blood pressure (hypertension) in patients, and by people with hypertension to monitor their blood pressure at home.
There are two types of blood pressure monitors: manual and automatic. Manual blood pressure monitors consist of a cuff that is inflated and deflated manually with a bulb and a stethoscope to listen to the blood flow. Automatic blood pressure monitors consist of a cuff that inflates and deflates automatically and displays the readings on a digital screen.
Some of the common applications of blood pressure monitors include:
- Diagnosis of hypertension: Blood pressure monitors are used by healthcare professionals to diagnose hypertension in patients and to monitor their blood pressure over time.
- Management of hypertension: Blood pressure monitors are used by people with hypertension to monitor their blood pressure at home and to make lifestyle changes or adjust their medications accordingly.
- Screening for high blood pressure: Blood pressure monitors are used in health screenings to detect high blood pressure in people who may not be aware they have it.
- Pulse oximeters
Pulse oximeters are medical devices used to measure the oxygen saturation level in a person’s blood. They are commonly used in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings to monitor patients’ oxygen levels and respiratory function, and by people with respiratory conditions to monitor their oxygen levels at home.
Pulse oximeters work by shining a light through a person’s fingertip or earlobe and measuring the amount of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin in the blood. The device then calculates the oxygen saturation level and displays it on a digital screen.

Some of the common applications of pulse oximeters include:
- Monitoring respiratory function: Pulse oximeters are used by healthcare professionals to monitor the oxygen levels and respiratory function of patients with respiratory conditions, such as asthma, COPD, and pneumonia.
- Monitoring during anesthesia: Pulse oximeters are used during surgery and other medical procedures to monitor the oxygen levels and respiratory function of patients who are under anesthesia.
- Monitoring during exercise: Pulse oximeters are used by athletes and people who exercise regularly to monitor their oxygen levels and ensure they are getting enough oxygen during physical activity
- Nebulizers
Nebulizers are medical devices that convert liquid medication into a fine mist that can be inhaled through a mask or mouthpiece. They are commonly used by people with respiratory conditions, such as asthma, COPD, and cystic fibrosis, to deliver medication directly to the lungs and airways.
Nebulizers work by using compressed air or ultrasonic vibrations to break up the liquid medication into a fine mist, which is then inhaled through a mask or mouthpiece. The medication is delivered directly to the lungs, where it can quickly and effectively relieve respiratory symptoms.
Some of the common applications of nebulizers include:
- Treatment of respiratory conditions: Nebulizers are commonly used to deliver medication to the lungs and airways to treat respiratory conditions, such as asthma, COPD, and cystic fibrosis.
- Relief of respiratory symptoms: Nebulizers can quickly and effectively relieve respiratory symptoms, such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath, by delivering medication directly to the lungs.
- Delivery of antibiotics: Nebulizers can also be used to deliver antibiotics directly to the lungs to treat respiratory infections, such as pneumonia.
- Surgical instruments
Surgical instruments are tools or devices that are used by healthcare professionals during surgical procedures to perform various tasks, such as cutting, dissecting, grasping, and suturing. These instruments are designed to be precise, durable, and easy to use, and are made from a variety of materials, such as stainless steel, titanium, and plastic.
Some of the most common surgical instruments include:
- Scalpels: A scalpel is a small, sharp knife used for making incisions in tissue.
- Forceps: Forceps are tweezers-like instruments used for grasping and holding tissue or objects during surgery.
- Scissors: Scissors are used for cutting tissue or materials during surgery.
- Retractors: Retractors are used to hold open an incision or wound to provide better access to the surgical site.
- Sutures: Sutures are used to close incisions or wounds after surgery.
- Surgical drills: Surgical drills are used to make holes in bone or to remove bone tissue during surgery.
- Endoscopes: Endoscopes are thin, flexible tubes with a light and camera attached that are used to view and perform surgery inside the body.
- CT scanners
CT (computed tomography) scanners are medical imaging devices that use X-rays and computer technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. They are commonly used in hospitals and clinics to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
CT scanners work by rotating an X-ray source and detector around the patient’s body, taking multiple X-ray images from different angles. These images are then processed by a computer to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body, which can be viewed on a computer screen or printed on film.
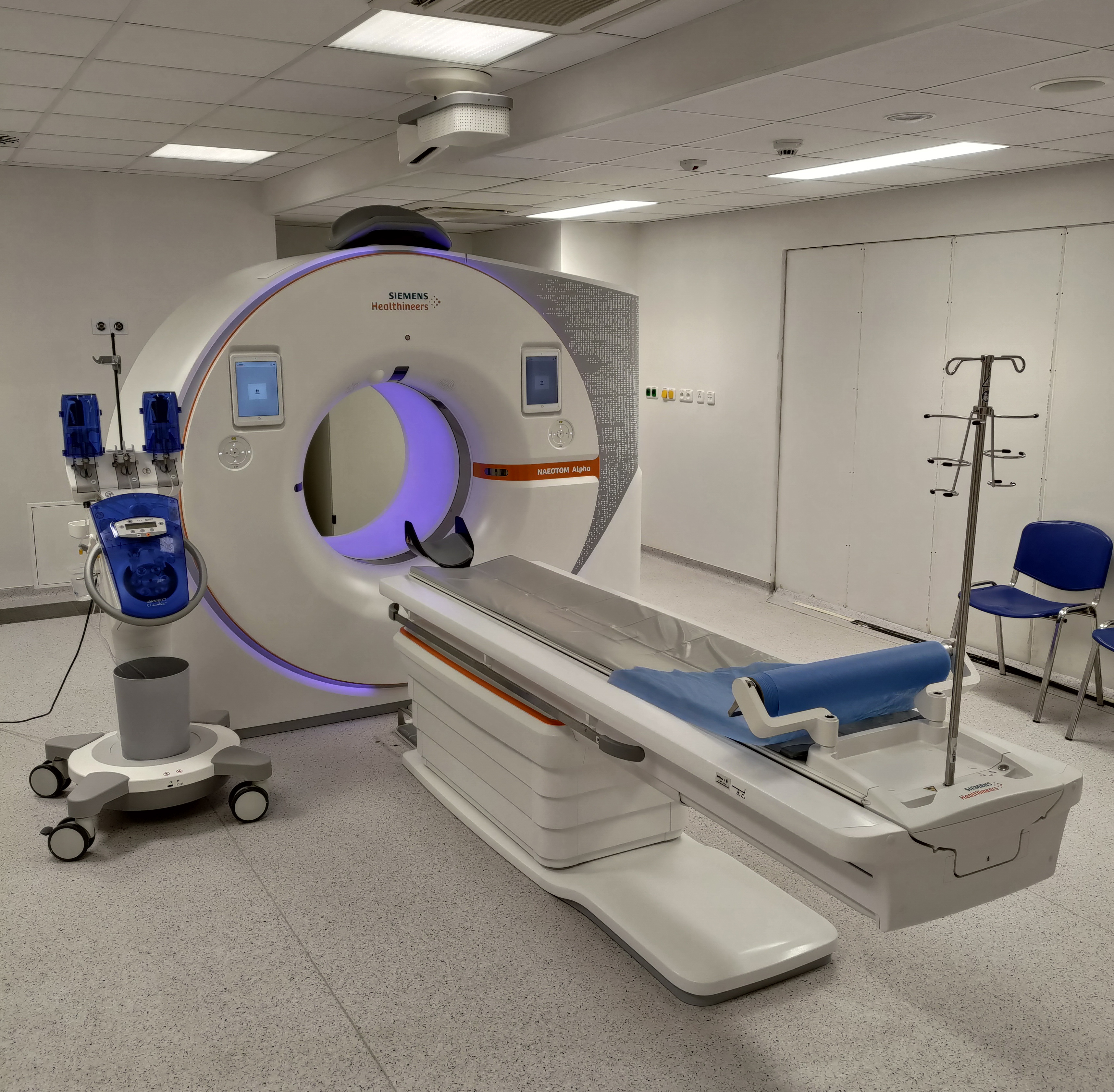
Some of the common applications of CT scanners include:
- Diagnosis of medical conditions: CT scans are commonly used to diagnose medical conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
- Monitoring of medical conditions: CT scans can be used to monitor the progress of medical conditions and track the effectiveness of treatment.
- Planning of medical procedures: CT scans can be used to plan medical procedures, such as surgery or radiation therapy.
- X-ray machines
X-ray machines are medical devices that use X-rays to produce images of the inside of the body. They are commonly used in hospitals and clinics to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions, such as broken bones, lung infections, and dental problems.
X-ray machines work by emitting a small amount of ionizing radiation through the body. The radiation passes through the body and is absorbed by different tissues and structures at different rates, depending on their density. The X-rays that pass through the body are detected by an X-ray detector, which produces an image of the internal structures.
Some of the common applications of X-ray machines include:
- Diagnosis of medical conditions: X-rays are commonly used to diagnose medical conditions, such as broken bones, lung infections, and dental problems.
- Monitoring of medical conditions: X-rays can be used to monitor the progress of medical conditions, such as osteoporosis.
- Planning of medical procedures: X-rays can be used to plan medical procedures, such as surgery or the placement of medical devices.
- MRI machines
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) machines are medical imaging devices that use a strong magnetic field, radio waves, and computer technology to create detailed images of the inside of the body. They are commonly used in hospitals and clinics to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions, such as cancer, neurological disorders, and musculoskeletal injuries.
MRI machines work by generating a strong magnetic field around the patient’s body, which causes the hydrogen atoms in the body’s tissues to align in a particular way. Radio waves are then used to cause these atoms to produce a signal, which is detected by the MRI machine and used to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures.
Some of the common applications of MRI machines include:
- Diagnosis of medical conditions: MRI scans are commonly used to diagnose medical conditions, such as cancer, neurological disorders, and musculoskeletal injuries.
- Monitoring of medical conditions: MRI scans can be used to monitor the progress of medical conditions and track the effectiveness of treatment.
- Planning of medical procedures: MRI scans can be used to plan medical procedures, such as surgery or radiation therapy.
- Dialysis machines
Dialysis machines are medical devices that are used to filter waste and excess fluid from the blood of patients with kidney failure. They work by mimicking the function of the kidneys, which normally filter waste and excess fluid from the blood.
Dialysis machines work by circulating the patient’s blood through a filter, which removes waste and excess fluid from the blood. The filtered blood is then returned to the patient’s body. There are two main types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Hemodialysis is the most common type of dialysis, and involves using an artificial kidney (dialyzer) and a dialysis machine to filter the blood. During hemodialysis, the patient’s blood is pumped through the dialyzer, which removes waste and excess fluid from the blood. The filtered blood is then returned to the patient’s body.
Peritoneal dialysis involves using the patient’s own abdominal lining (peritoneum) as a filter. During peritoneal dialysis, a special solution is introduced into the patient’s abdomen, where it remains for several hours. The solution draws waste and excess fluid from the blood into the peritoneum, where it can be drained out of the body.


