All you need to know about E-wallets in India in 2021 – being tech savvy

E-Wallets: India is slowly moving towards a cashless economy. Demonetization was one of the biggest steps took by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on November 8, 2016.
The movement of cashless India started before declaring demonetization. They created the base by
(1) Introducing financial inclusion Jandhan Yojana
(2) Giving license to payment bank
(3) Promoting mobile banking
Almost every country in the world follows a cashless economy. According to the research, in Sweden only 3% of people do cash transactions, Belgium 93% of the population does a cashless transaction, in Denmark 1/3 population do mobile banking, in Norway many banks don’t give cash to users.
Many banks have moved their step towards online banking along with the progress of digital India and the cashless economy. There has been tremendous growth in the e-banking sector the usage of e-wallet has increased in 2020. Due to the restricted movement of consumers, there was a minimal transaction in cash which led to a rise in the number of consumers using an e-wallet.

What is an e-wallet?
An E-wallet is an electronic wallet. Its utility is as same as debit/credit card just provides a payment option in an electronic form. Payment can be made through smartphones and computers. The main objective of an e-wallet is to provide paperless transactions and to make it easier and convenient.
E-wallets are classified into two main components information and software. The information shows all the databases of the consumers, Payment Methods, Debit/credit amount paid. Whereas Software stores all the personal information and provides encryption and security of data.
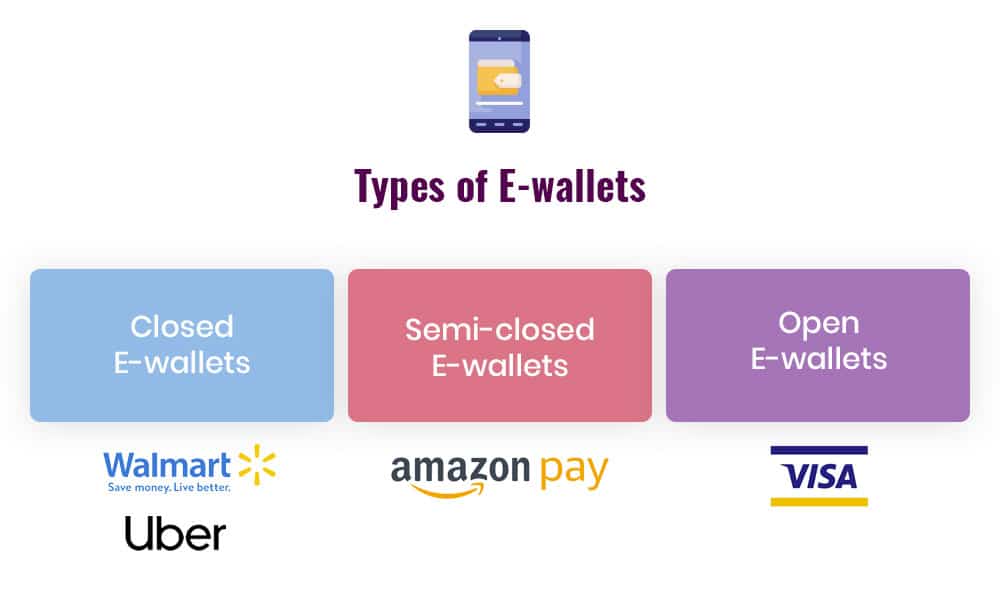
E-wallets are classified into three different categories:-
 Here are different sorts of transactions you’ll do through digital wallets.
Here are different sorts of transactions you’ll do through digital wallets.
- Closed e-Wallets: This is one of the simplest forms of Digital wallets as they are only limited to the payment of particular websites and are restricted to any outside payments like Walmart. Since it has restricted to a particular mode of transaction, it is named a closed e-wallet.
- Semi-Closed e-Wallets: these offer more variety of payment as compared to closed e-wallets. They allow the user to make payments in apps and are also associated with the payments at local stores and restaurants. However, their services are not available at every payment medium and have limited reach up to the consumers.
- Open e-Wallets: These type of wallet provide one of the easiest ways for money transaction as it is not limited to any websites or app. The only condition for the transaction of money in an open wallet is the user must be using the same app it becomes easier for the sender and receiver to transact money as it provides the service of payment anywhere, anytime.
What are the challenges that affected the rate of adoption of e-wallets?
- Internet connectivity issues:- According to research, only 33% of the population has access to the internet. It is difficult for Indian consumers to opt for e-banking due to a lack of internet connectivity issues. There are still some rural areas in India that are completely unaware of e-wallets and their uses. 97% of the population have never used e-wallets in a rural area.
- Security issues:- Since using an e-wallet includes sharing essential credit/debit card details it becomes uneasy for the consumer to disclose the information. As there has been tremendous growth in the number of cybercrimes the banking information disclosed to e-wallet platforms can also be used for illegal operations by hackers. Hence these e-wallet companies need to ensure cybersecurity.
- Interoperability:- There is no option available to transfer money from one e-wallet to another. This has been an issue for the consumer and has been addressed by them at different forums.
Top 3 e-wallets in India

- Paytm:- An e-wallet startup company launched in 2009 has over 100m active users in India with 75m transactions per month. Paytm ranks in the top 7 e-commerce companies in India. Currently, it offers a wide range of payment options that is from mobile recharge to purchasing apparel at the same platform. China’s Alibaba Group is affiliated with Paytm and is said to be invested USD 80m in September 2015. They raise their stake to 40% and increased their valuation to USD 4 billion.

- Mobiwik:- This was launched in 2009 by Bipin Preet Singh and Upasana Taku Singh. Both couples graduated from IIT and seeded their e-wallet startup with their investments of USD 250. They initially had a closed wallet facility. To make their wallet more accessible they partnered with merchants. After that Mobiwik also approached various websites to use their payment facility. MobiKwik was said to be the biggest competitor of Paytm. In 2015, they partnered with Uber India and enabled the drivers to use their e-wallet and also debit/credit payment.

- Freecharge:- This e-wallet provides the consumer with various payment options as such investment and lendings, savings, insurance, payments(electricity, gas, telephone bill). On April 8, 2015, Snapdeal acquired Freecharge for USD 400m it is said to be the second-biggest takeover after Ibbio by the biggest rival Make my trip. In July 2017 Axis bank acquired Freecharge for USD 60m.
What do I need to start with an e-wallet service?
- Your bank account should be linked with the mobile number from which you will be using an e-wallet.
- A good internet connection
- Any e-wallet app you are willing to use.
What are the must-do practices while using an e-wallet?
- Make sure you don’t share your banking details with anyone
- Register your phone number with the bank to get information about each transaction carried through SMS.
- Transaction should be carried out only with a trusted merchant.
Digital wallet has gained a major boost during the pandemic. The majority of the Prepaid Payment Instruments(PPI) are done through mobile wallets. Offering various benefits such as accessibility, acceptable and convenience has made the consumers shift to e-wallet. Digital wallet somewhere supports the growth and development of the nation by making India a paperless/cashless economy. The youth is more aware of changes that lead to digitalization following the development of the country.
Edited by Sanjana Simlai.




