
Medical devices in the field of biomedical engineering are instruments, machines, implants, or any other similar apparatus that are used for the diagnosis, treatment, or prevention of medical conditions. These devices are designed to improve the quality of life for patients and to aid healthcare professionals in providing better care.
Medical devices can range from simple devices such as bandages and tongue depressors to complex machines like MRI scanners and pacemakers. They can be used for a variety of purposes, such as monitoring vital signs, performing diagnostic tests, administering medication, or delivering therapies.
Biomedical engineering is the field of engineering that applies engineering principles to healthcare and medical technology. Biomedical engineers design, develop, and improve medical devices and equipment, as well as develop new diagnostic and therapeutic procedures.
some of the most commonly used and popular medical devices in India:
- CT scanners
CT (Computed Tomography) scanners are medical devices that use X-ray technology to produce detailed images of the inside of the body. They are widely used for diagnostic purposes in various medical specialties, such as oncology, neurology, cardiology, and emergency medicine.
CT scanners work by rotating an X-ray tube around the patient’s body, while detectors on the other side of the patient measure the X-rays that pass through the body. The data collected from multiple angles is then processed by a computer to produce cross-sectional images of the body.
CT scanners are often used to diagnose conditions such as tumors, fractures, and infections, as well as to guide interventional procedures such as biopsies and drainage. They can also be used to monitor the progress of treatment and to detect any changes in the body over time.
- MRI machines
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines are medical devices that use a magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to produce detailed images of the inside of the body. They are commonly used for diagnostic purposes in various medical specialties, such as neurology, orthopedics, and oncology.
MRI machines work by creating a strong magnetic field around the patient’s body, which causes the hydrogen atoms in the body’s tissues to align in a specific way. Radio waves are then used to disrupt this alignment, causing the hydrogen atoms to emit a signal that can be detected by the MRI machine’s detectors. The data collected from multiple angles is then processed by a computer to produce detailed images of the body.
MRI machines can be used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including tumors, infections, and structural abnormalities. They are also useful in evaluating the extent of injuries and tracking the progress of treatment.
- Ultrasound machines
Ultrasound machines are medical devices that use high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the inside of the body. They are commonly used for diagnostic purposes in various medical specialties, such as obstetrics and gynecology, cardiology, and gastroenterology.
Ultrasound machines work by transmitting high-frequency sound waves into the body, which bounce off the internal structures and return to the machine as echoes. The echoes are then processed by the machine’s computer to produce real-time images of the body.

Ultrasound machines are often used to diagnose conditions such as tumors, cysts, and other abnormalities. They are also useful in evaluating blood flow, detecting blockages in blood vessels, and guiding interventional procedures such as biopsies and drainages.
- X-ray machines
X-ray machines are medical devices that use electromagnetic radiation to produce images of the inside of the body. They are widely used for diagnostic purposes in various medical specialties, such as orthopedics, cardiology, and radiology.
X-ray machines work by directing a beam of high-energy radiation through the body, which is absorbed differently by different tissues in the body. The radiation that passes through the body is then detected by a sensor on the other side of the body, which creates an image based on the amount of radiation that was absorbed.
X-ray machines are often used to diagnose conditions such as bone fractures, lung infections, and dental problems. They are also useful in detecting abnormalities in the chest, abdomen, and extremities.
- Hematology analyzers
Hematology analyzers are medical devices that are used to analyze blood samples for various parameters, such as the number and type of blood cells, and the levels of hemoglobin and other blood components. They are commonly used in clinical laboratories and hospitals for diagnostic purposes.
Hematology analyzers work by analyzing the physical and chemical properties of the blood sample. They use various techniques such as impedance, light scattering, and flow cytometry to determine the number, size, and shape of blood cells. They also measure the levels of various blood components such as hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelets.
Hematology analyzers are used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, such as anemia, infections, blood disorders, and certain types of cancer. They can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to track the progress of certain diseases.
- ECG machines
ECG (Electrocardiogram) machines are medical devices that are used to measure and record the electrical activity of the heart. They are commonly used in hospitals, clinics, and ambulatory settings for diagnostic purposes.
ECG machines work by recording the electrical activity of the heart through electrodes that are attached to the skin on the chest, arms, and legs. The electrodes detect the electrical impulses that are generated by the heart, which are then amplified and recorded by the machine. The resulting ECG waveform shows the timing and strength of each electrical impulse, which can help diagnose various heart conditions.

ECG machines are used to diagnose a wide range of heart conditions, such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and congenital heart disease. They can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to track the progress of certain heart conditions.
- Ventilators
Ventilators are medical devices that are used to provide mechanical ventilation to patients who are unable to breathe on their own or who require assistance with breathing. They are commonly used in intensive care units, emergency departments, and operating rooms.
Ventilators work by delivering a mixture of air and oxygen into the lungs through a tube that is inserted into the patient’s airway. The machine regulates the volume and rate of air that is delivered, and may also control the amount of oxygen that is delivered. Ventilators can be set to various modes and settings, depending on the patient’s condition and the desired outcome.
Ventilators are used to support patients who have respiratory failure, such as those with acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumonia, or COPD. They can also be used during surgical procedures or to support patients who are in a medically-induced coma.
- Dialysis machines
Dialysis machines: Dialysis machines are medical devices used to filter and remove waste and excess fluid from the blood of patients with kidney failure. They work by pumping the patient’s blood through a series of filters and returning the filtered blood to the patient’s body. Dialysis machines are commonly used in hospitals and dialysis centers to treat patients with chronic kidney disease.
Blood glucose monitors: Blood glucose monitors are medical devices used to measure the level of glucose in a patient’s blood. They are commonly used by patients with diabetes to monitor.
Dialysis machines are an essential tool for patients with kidney failure, as they help to remove waste and excess fluid from the blood, which can cause serious health complications. They are often used in conjunction with other treatments, such as medication and dietary changes, to help manage the symptoms of kidney failure.
- Blood glucose monitors
Blood glucose monitors are medical devices used to measure the level of glucose in a patient’s blood. They are commonly used by patients with diabetes to monitor their blood glucose levels and adjust their medication and lifestyle accordingly.
Blood glucose monitors work by using a small lancet to prick the patient’s finger and obtain a small drop of blood. The blood is then placed on a test strip, which is inserted into the blood glucose monitor. The monitor analyzes the blood and provides a reading of the patient’s blood glucose level.

Blood glucose monitors can be found in various sizes and with different features, such as Bluetooth connectivity, memory storage, and continuous glucose monitoring. They are commonly used by patients with diabetes to manage their condition, and can be used at home, at work, or on the go.
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is important for patients with diabetes, as it can help them avoid serious health complications, such as hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Blood glucose monitors allow patients to track their blood glucose levels and make informed decisions about their medication, diet, and lifestyle.
- Insulin pumps
Insulin pumps are medical devices used to deliver insulin to patients with diabetes. They are small, battery-operated devices that are worn outside the body and connected to a small tube or catheter that is inserted under the skin. Insulin pumps deliver a continuous stream of insulin into the body, which can be adjusted to match the patient’s insulin needs.
Insulin pumps work by using a small computerized device that controls the flow of insulin into the body. The patient inputs information about their insulin needs, such as their basal rate (the amount of insulin needed between meals) and bolus doses (the amount of insulin needed to cover meals and snacks).
Insulin pumps can also be programmed to deliver different types of insulin at different times of day, which can help patients maintain better control over their blood glucose levels. Some insulin pumps also have features such as automatic shutoff in case of low blood glucose levels, alarms, and data tracking capabilities.
- Infusion pumps
Infusion pumps work by using a motorized mechanism to control the flow rate of fluids or medications through an intravenous (IV) catheter. The pump can be programmed to deliver a specific dose or rate of infusion over a set period of time.
There are several different types of infusion pumps, including volumetric pumps, syringe pumps, and ambulatory pumps. Volumetric pumps are designed to deliver a precise volume of fluid over a set period of time, while syringe pumps are used to deliver small volumes of medication or fluids. Ambulatory pumps are portable and can be worn by patients to deliver medication or fluids over an extended period of time, such as during chemotherapy.
- Surgical instruments
Surgical instruments are medical devices used during surgical procedures to cut, dissect, grasp, or manipulate tissues or organs. They are essential tools for surgeons and other medical professionals, and are designed to be precise, durable, and reliable.
Surgical instruments come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and are designed for specific surgical procedures. Some common types of surgical instruments include:
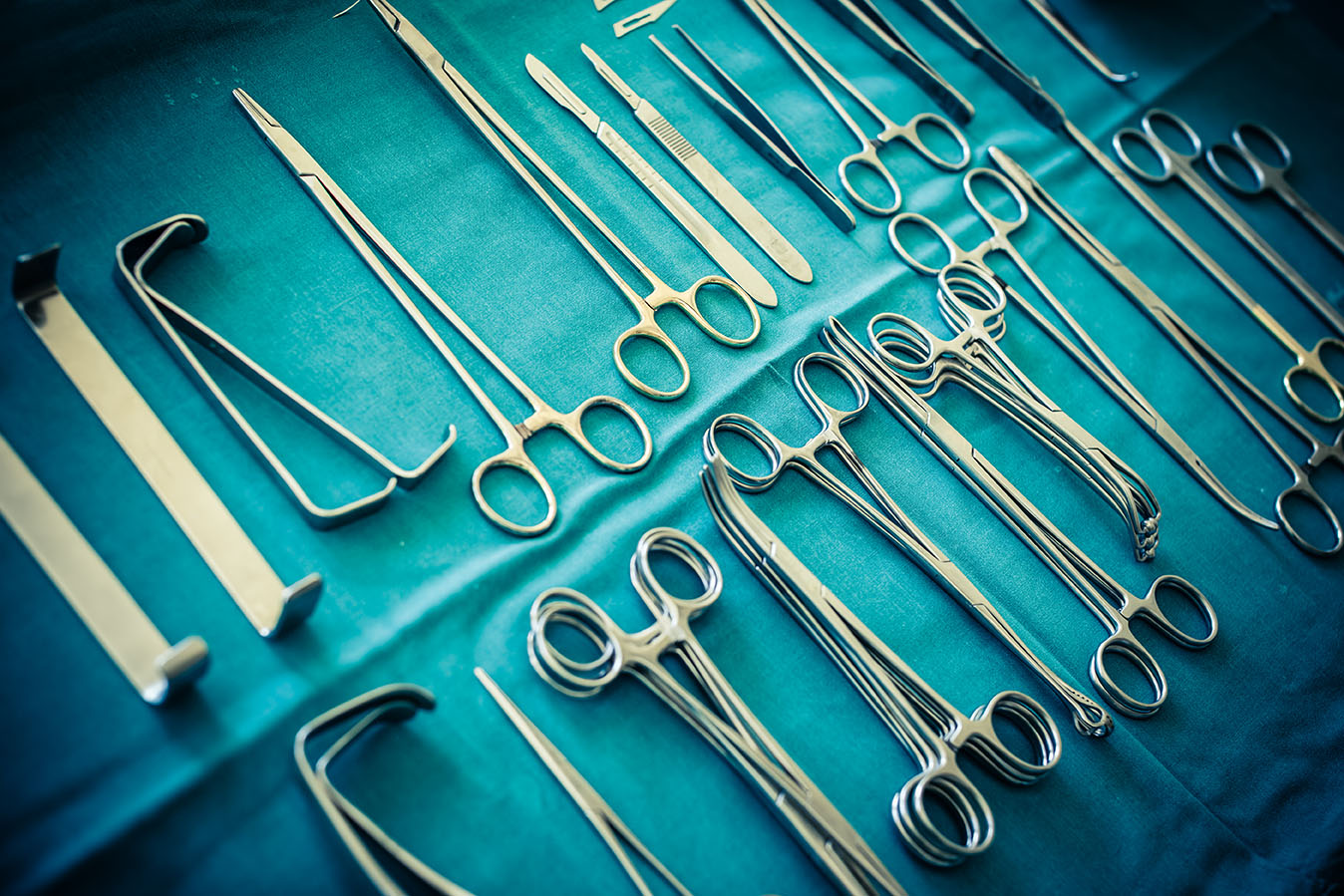
- Scalpels – used for cutting tissue and making incisions
- Forceps – used for grasping and holding tissues or objects
- Scissors – used for cutting tissue and sutures
- Retractors – used for holding tissues or organs out of the way during surgery
- Needle holders – used for holding needles during suturing
- Suction devices – used for removing blood and other fluids during surgery
- Electrocautery devices – used for sealing blood vessels and cutting tissue using heat
- Patient monitoring systems
Patient monitoring systems are medical devices used to continuously monitor a patient’s vital signs and other important health information. They are used in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings to help healthcare professionals track a patient’s condition and detect any changes or abnormalities.
Patient monitoring systems typically include a range of sensors and devices that are attached to the patient’s body, such as electrodes for measuring heart rate and rhythm, a blood pressure cuff, a pulse oximeter for measuring oxygen saturation in the blood, and a thermometer for measuring temperature. These sensors are connected to a monitor or computer that displays the patient’s vital signs in real time.
In addition to monitoring vital signs, patient monitoring systems may also include other features such as alarms to alert healthcare professionals of changes in the patient’s condition, data storage for tracking changes over time, and wireless connectivity for remote monitoring.
- Blood pressure monitors
Blood pressure monitors are medical devices used to measure a patient’s blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood throughout the body. Blood pressure monitors are used to measure two numbers: systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number). Blood pressure is typically measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
There are two main types of blood pressure monitors: manual and automatic. Manual blood pressure monitors require a healthcare professional to use a stethoscope and a cuff that is wrapped around the patient’s arm to listen to the pulse and measure blood pressure. Automatic blood pressure monitors are electronic devices that use a cuff and a sensor to automatically measure blood pressure.
Some blood pressure monitors are designed for home use, allowing patients to monitor their blood pressure regularly and track changes over time. These devices may include features such as memory storage for tracking measurements, and may be connected to a smartphone app for tracking and sharing data with healthcare providers.
- Pulse oximeters
Pulse oximeters are medical devices used to measure the oxygen saturation (SpO2) of a patient’s blood. Oxygen saturation is the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is carrying oxygen. Pulse oximeters work by shining a light through a patient’s finger or earlobe and measuring the amount of light that is absorbed by the blood.
Pulse oximeters are commonly used in hospitals and other healthcare settings to monitor patients with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions, such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or heart failure. They are also used to monitor patients during surgery or anesthesia.
Pulse oximeters are small, portable devices that can be used at home by patients with chronic respiratory or cardiovascular conditions. They are often used by patients with sleep apnea to monitor their oxygen levels during sleep.



