ISRO’s Aditya-L1 Mission: Unlocking Solar Mysteries from the Harmonious Lagrange Point
ISRO's Aditya-L1 Mission: Unlocking Solar Mysteries from the Harmonious Lagrange Point

ISRO’s Aditya-L1 Mission: Unlocking Solar Mysteries from the Harmonious Lagrange Point
In a groundbreaking leap towards unraveling the enigmatic nature of our nearest star, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is gearing up for its much-anticipated Aditya-L1 mission. With a focus on exploring the Sun’s atmosphere and magnetic fields, the mission is set to provide unprecedented insights into the Sun’s behavior and its impact on space weather. A key element of this mission lies in the Lagrange Point, a celestial location of remarkable equilibrium that allows Aditya-L1 to observe the Sun continuously, free from Earth’s interference.
Unveiling the Lagrange Points
The Lagrange Points, named after the 18th-century mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange, are five unique positions in space where the gravitational forces of a two-body system, such as the Earth and the Moon or the Earth and the Sun, produce enhanced regions of attraction and repulsion. These points, denoted as L1, L2, L3, L4, and L5, mark positions where the gravitational pull of the two bodies creates a stable triangular formation, allowing smaller objects, like satellites and spacecraft, to essentially “hover” in relation to the larger bodies.

The Mighty L1 Lagrange Point
At the heart of ISRO’s Aditya-L1 mission is the L1 Lagrange Point, located about 1.5 million kilometers (0.93 million miles) from Earth. This prime spot offers a unique advantage: it allows the spacecraft to maintain a synchronized orbit with Earth as it orbits the Sun. Imagine this point as a stationary vantage point where the gravitational forces of the Earth and the Sun balance out, letting the spacecraft effectively station itself in a way that keeps an eye on the Sun without Earth getting in the way.
Why L1?
The choice of L1 for Aditya-L1 is strategic. It grants the spacecraft an uninterrupted view of the Sun. Unlike Earth-based observatories, Aditya-L1 isn’t bound by the day-night cycle or atmospheric interference, allowing it to capture a comprehensive and continuous dataset of the Sun’s behavior. This is particularly crucial in studying the Sun’s outermost layer, the corona, which emits the Sun’s powerful solar wind, a stream of charged particles that can influence space weather and impact technologies on Earth.
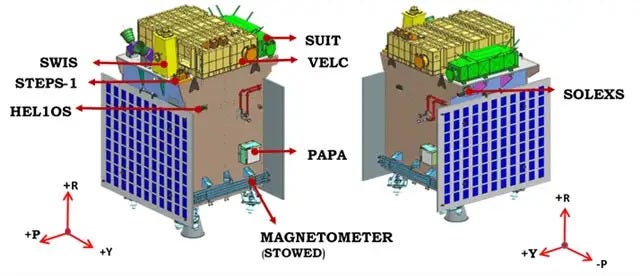
Unlocking Solar Mysteries
The Sun, while vital for sustaining life on Earth, harbors mysteries that scientists are still working to comprehend. Its behavior isn’t just about sunshine; it’s about solar flares that release massive bursts of energy, coronal mass ejections that can disrupt power grids and communication systems, and the intricate dance of magnetic fields that drive these phenomena. Aditya-L1 aims to decode these mysteries by observing the Sun’s corona and its magnetic fields up close.
The Sun-Earth Connection
Understanding the Sun is pivotal for understanding our own planet’s environment. The Sun’s activity can influence Earth’s space environment, giving rise to the fascinating realm of space weather. Solar storms, driven by the Sun’s eruptions, can have real-world impacts, from disrupting GPS signals to affecting power distribution systems. Aditya-L1’s observations from the vantage point of L1 will help scientists create more accurate models to predict and prepare for space weather events.
Challenges and Innovations
Launching a spacecraft to a Lagrange Point isn’t a simple feat. Aditya-L1 has to overcome the immense challenge of traveling a considerable distance from Earth and navigating through complex gravitational forces. ISRO’s engineers have meticulously planned the trajectory and propulsion systems to ensure the spacecraft reaches its destination with precision. This venture showcases India’s technological prowess in conquering new frontiers of space exploration.
International Collaborations and Contributions
Space exploration often transcends national borders, and Aditya-L1 is no exception. ISRO has collaborated with international space agencies and research institutions to enhance the mission’s scientific potential. This collaboration not only fosters knowledge-sharing but also underscores the global significance of understanding the Sun and its effects on our solar system.
Anticipating Discoveries
As Aditya-L1 prepares to journey to the L1 Lagrange Point, scientists, space enthusiasts, and curious minds alike await the revelations it will bring. From deciphering the Sun’s magnetic activity to gaining insights into the origins of solar wind, this mission holds the promise of reshaping our understanding of the Sun and its profound influence on our cosmic neighborhood.

Conclusion
ISRO’s Aditya-L1 mission is poised to mark a significant milestone in solar exploration. By capitalizing on the unique advantages of the Lagrange Point L1, the spacecraft is set to provide an unprecedented window into the Sun’s behavior and its connection to our planet. As humanity’s quest for knowledge propels us ever deeper into the cosmos, Aditya-L1 stands as a shining example of human ingenuity and international collaboration, reminding us that the universe’s most profound mysteries are within our reach.




