Deadly Bangladesh Strain of Nipah Virus Claims 90% of Infected Lives: Urgent Actions Required, Says Ex-ICMR Scientist

Deadly Bangladesh Strain of Nipah Virus Claims 90% of Infected Lives: Urgent Actions Required, Says Ex-ICMR Scientist
In a grave public health concern, the Bangladesh strain of the Nipah virus has emerged as an alarming threat, claiming a staggering 90% of lives among those infected, according to Dr. Raman Gangakhedkar, a prominent epidemiologist and former head scientist at the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). This revelation has sent shockwaves through the medical community, necessitating immediate and comprehensive measures to combat its spread and mitigate its impact.
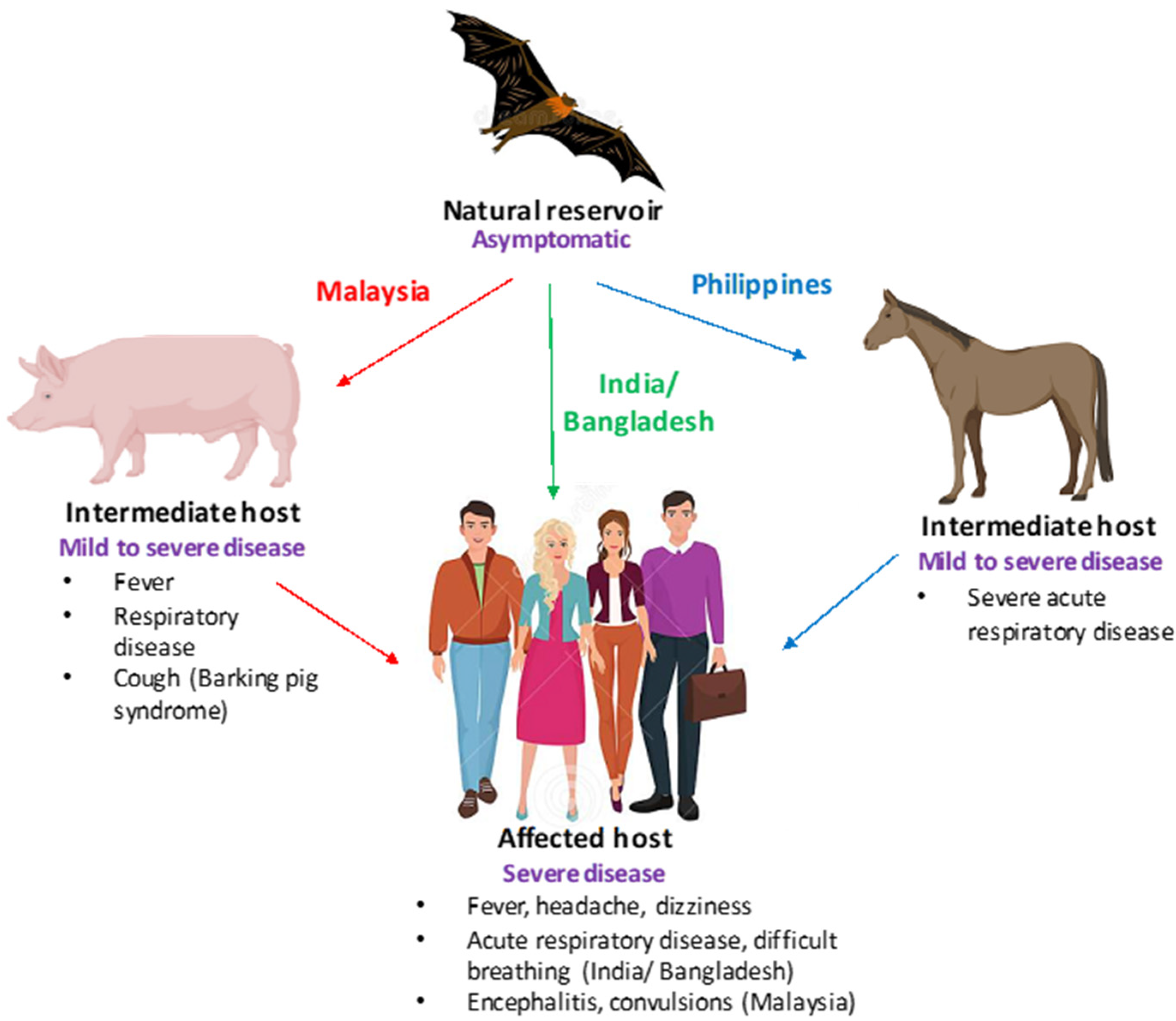
The Nipah virus, known for its high mortality rate, has posed a formidable challenge for healthcare authorities across the globe since its discovery in Malaysia in 1999. However, the virulence of the Bangladesh strain, which is now under intense scrutiny, has raised unprecedented concerns.
Understanding the Lethality of the Bangladesh Nipah Virus Strain
The Bangladesh strain of the Nipah virus, as disclosed by Dr. Gangakhedkar, is characterized by a rapid onset of symptoms, with breathlessness being a prominent and distressing feature. This development is particularly alarming, as the virus has traditionally been associated with flu-like symptoms such as fever, cough, and sore throat. The sudden and severe respiratory distress observed in infected individuals has placed immense strain on healthcare systems, calling for immediate action.
Moreover, the grim statistic that this strain claims the lives of 9 out of 10 infected persons is deeply concerning. This places it among the deadliest viruses known to humankind, surpassing even some of the most notorious infectious diseases in terms of mortality. Such a high fatality rate underscores the urgent need for a coordinated and well-planned response.

Urgent Priorities in Tackling the Nipah Virus Crisis
Dr. Gangakhedkar has outlined key priorities that must be addressed swiftly and effectively to contain the spread of the Bangladesh strain of the Nipah virus:
1. Finding the Index Patient: Identifying the first person infected, known as the index patient, is crucial in understanding the source and initial spread of the virus. This information can aid in devising containment strategies and preventing future outbreaks.
2. Origin Tracing: Determining the origin of the Nipah virus is imperative for preventing its recurrence. Investigating the sources, whether it be animals or other vectors, is essential to break the chain of transmission.
3. Animal Testing: Rigorous testing of animals in the affected regions is necessary to ascertain if they serve as reservoirs or intermediate hosts for the virus. This step is vital in preventing further transmission from animals to humans.
4. Community Mobilization: Engaging and educating the local communities is crucial for effective disease control. Promoting awareness about the virus, its symptoms, and preventive measures can empower individuals to protect themselves and others.
5. Medical Preparedness: Ensuring that healthcare facilities are well-equipped and staffed to handle Nipah virus cases is paramount. Adequate medical aid, including ventilators and antiviral medications, must be readily available to provide timely and effective treatment.
Global Collaboration and Vigilance
The emergence of such a deadly Nipah virus strain in Bangladesh serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of our world and the need for global collaboration in public health efforts. As nations grapple with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the appearance of another lethal virus underscores the importance of vigilance and preparedness.
International organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO), must play a central role in coordinating efforts to combat the Nipah virus. Information sharing, research collaboration, and resource allocation are critical components of a global response to this emerging threat.

Conclusion: A Race Against Time
The revelation of the Bangladesh strain of the Nipah virus, with its horrifyingly high mortality rate, is a stark wake-up call to the world. It demands swift and decisive action on multiple fronts, from identifying the index patient to mobilizing communities and ensuring medical preparedness.
This crisis underscores the importance of investing in infectious disease research, surveillance, and response systems. The tragic toll of the Nipah virus in Bangladesh serves as a grim reminder that emerging infectious diseases continue to pose a significant threat to global health security.
In the race against time to contain the Bangladesh Nipah virus strain, the world must come together, pool its resources, and deploy its best scientific minds to prevent further loss of life and safeguard the health and well-being of our communities. Only through collective action can we hope to overcome this deadly threat and emerge stronger in the face of future challenges.




