Top 20 Best Military & International Affairs In India 2023
Top 20 Best Military & International Affairs In India 2023

Top 20 Best Military & International Affairs In India 2023
International and military affairs refer to the relationships, interactions, and activities between nations, as well as the military activities and strategies of nations, in the global arena. It encompasses a wide range of issues including diplomacy, security, trade, and conflict resolution.
International affairs and military strategy are critical components of a country’s foreign policy and shape its interactions with other nations and its role in global affairs. These fields are constantly evolving and are influenced by a variety of factors such as economic conditions, political changes, and technological advancements.
Understanding international and military affairs is crucial for nations to maintain their national security and prosperity, and to foster cooperation and stability in the international community.
Military and international affairs are significant aspects of India’s foreign policy. India has one of the largest military forces in the world, and its military plays a key role in maintaining regional and global stability.
India’s military is equipped with modern weapons and technology and has a long history of participating in United Nations peacekeeping missions.
India’s foreign policy is guided by its vision of being a responsible and leading global power and is shaped by several factors including economic, strategic, and political considerations. India’s international relations are characterized by strong ties with its neighbors, close relationships with major world powers such as the United States and China, and active participation in regional and global organizations such as the United Nations, the World Trade Organization, and the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) grouping.
In recent years, India has increasingly been focused on expanding its economic and strategic partnerships, both regionally and globally. India’s “Act East” policy, for example, aims to deepen its engagement with Southeast Asian countries, while its “Look West” policy seeks to expand ties with the Persian Gulf and West Asian regions.
Overall, military and international affairs play a crucial role in shaping India’s place in the world and its ability to advance its national interests in a rapidly changing global environment. Here are 20 current military and international affairs affecting India:
India-China border disputes
India-Pakistan relations and border conflicts
India’s role in regional and global security initiatives
India’s defense modernization and procurement
India’s counterterrorism efforts
India’s participation in UN peacekeeping missions
India-US defense ties and cooperation
India’s relations with neighboring countries (e.g. Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka)
India’s nuclear policy and stance on non-proliferation
India’s space program and military applications of space technology
India’s stance on regional and global terrorism
India-Russia defense and security cooperation
India’s role in regional and international organizations (e.g. BRICS, SAARC, UN)
India’s economic and trade relations with other countries
India’s energy security and dependence on foreign sources of energy
India’s cyber security policies and initiatives
India’s maritime security and territorial disputes in the Indian Ocean region
India’s human rights record and relationship with minority groups
India’s efforts to address climate change and environmental sustainability
India’s role in resolving regional conflicts and promoting peace and stability.
India-China border disputes

India-China border disputes refer to the ongoing territorial and boundary disputes between India and China over their border areas. The disputes date back to the colonial era and have resulted in several small-scale military conflicts, including the 1962 Sino-Indian War.
In recent years, tensions have escalated along the disputed border, particularly in the Ladakh region, leading to a military standoff in 2020. The two countries have engaged in talks to resolve the disputes, but a final resolution has not been reached.
Border disputes are a complex issue, involving multiple territorial claims, historical and cultural differences, and strategic interests. They have significant implications for regional stability and security, as well as for the bilateral relationship between India and China.
India-Pakistan relations and border conflicts
India-Pakistan relations have been fraught with conflict and tension since the two countries gained independence from British rule in 1947. One of the main sources of tension between the two nations is the disputed region of Kashmir, which has been the subject of numerous wars and skirmishes over the years.
In recent years, the relationship between India and Pakistan has been characterized by sporadic outbreaks of violence along the border, as well as incidents of terrorism, particularly in the Indian-administered region of Jammu and Kashmir. The two countries have engaged in several rounds of peace talks over the years, but a lasting resolution to their differences has yet to be reached.
The India-Pakistan border conflicts have far-reaching implications for regional stability and security, as well as for the economic and social well-being of the people living in the region. The conflicts have also fueled tensions between the two countries and have often resulted in a suspension of diplomatic and trade relations
India’s role in regional and global security initiatives

India plays an important role in regional and global security initiatives. As one of the largest and most populous countries in South Asia, India has a significant impact on regional stability and security. It is also a member of several international organizations, including the United Nations (UN), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and the G20, among others.
In terms of regional security, India is an active participant in the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) and has taken steps to improve relations with its neighboring countries, such as Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and Sri Lanka. India is also a key player in regional forums such as the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) and the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
At the global level, India has been a strong advocate of multilateralism and has played an active role in UN peacekeeping operations. It is also a member of various international coalitions and partnerships aimed at promoting peace, security, and stability, such as the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) and the BRICS grouping (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa).
India’s role in regional and global security initiatives is important for maintaining stability, promoting economic development, and addressing common security challenges, such as terrorism and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
India’s defense modernization and procurement
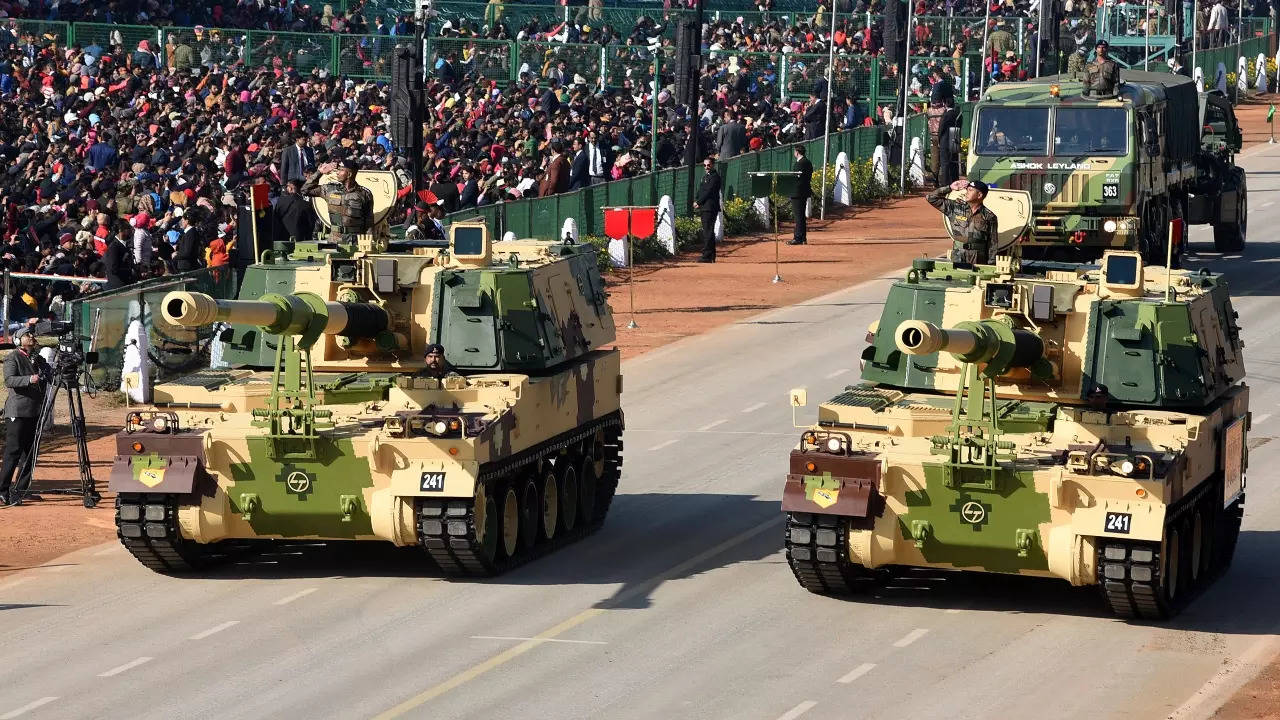

India’s defense modernization and procurement refers to the efforts by the Indian government to modernize its armed forces and equip them with the latest technology and equipment. This is a crucial aspect of India’s national security strategy, as it seeks to ensure the readiness and capabilities of its military to respond to a wide range of threats and challenges.
India is one of the largest defense spenders in the world and has undertaken significant efforts to upgrade its defense infrastructure, including the development of advanced weapons systems, the establishment of defense production units, and the modernization of its military training and education programs.
India has also launched major procurement programs to acquire new equipment, such as fighter jets, submarines, and helicopter gunships, among others.
India’s defense modernization and procurement initiatives are driven by several factors, including the need to address gaps in its defense capabilities, respond to evolving security threats, and improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of its military.
These initiatives are also a key aspect of India’s overall economic development strategy, as they provide opportunities for local industries and technology companies to grow and contribute to the national economy.
Overall, India’s defense modernization and procurement efforts are an important aspect of its national security and economic development and are critical to ensuring the readiness and capabilities of its armed forces.
India’s counterterrorism efforts

India’s counterterrorism efforts refer to the actions taken by the Indian government and security forces to counter terrorism and prevent acts of terrorism within its borders. This is a critical aspect of India’s national security strategy, as terrorism continues to pose a major threat to the stability and security of the country.
India’s counterterrorism efforts include a range of measures, such as intelligence gathering and analysis, enhanced border security, targeted military operations, and the development of specialized units and agencies to address the threat of terrorism.
The government has also taken steps to strengthen its legal framework and enhance inter-agency cooperation to more effectively address the threat of terrorism.
In recent years, India has also sought to improve its counterterrorism cooperation with international partners, including the United States and other countries in the region, to better address the threat of terrorism and extremism.
This has included sharing intelligence and other information and working together to disrupt transnational terrorist networks.
India’s counterterrorism efforts have resulted in some successes, including the disruption of several major terrorist plots and the capture or killing of several high-profile terrorists. However, the threat of terrorism continues to persist, and India remains vigilant in its efforts to counter this threat and protect its citizens and its national security
India’s participation in UN peacekeeping missions

India has been a significant contributor to United Nations (UN) peacekeeping missions and has participated in several such missions around the world. These missions are aimed at promoting peace and security, protecting civilians, and helping to create the conditions for the restoration of peace and stability in conflict-affected regions.
India has a long history of participation in UN peacekeeping missions, and its troops and police personnel have played a critical role in several operations, including in Somalia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, East Timor, and Haiti, among others.
India has also contributed to the development of the UN peacekeeping doctrine and has provided training and capacity-building support to other peacekeeping contributors.
India’s participation in UN peacekeeping missions reflects its commitment to promoting peace and stability around the world, and to support the efforts of the international community to address global security challenges.
India sees peacekeeping as an important aspect of its foreign policy and as a means to demonstrate its support for the principles and values of the UN Charter.
Overall, India’s participation in UN peacekeeping missions is an important aspect of its role in the international community and its commitment to promoting peace, security, and stability around the world.
India-US defense ties and cooperation

India and the United States have developed a strong defense relationship in recent years, with a growing focus on cooperation in areas such as defense technology and equipment, counterterrorism, and regional security.
This relationship is seen as an important aspect of the overall strategic partnership between the two countries and has been driven by several factors, including shared security interests and the growing importance of India in the Indo-Pacific region.
In terms of defense cooperation, the two countries have held several high-level bilateral and multilateral dialogues, and have signed several agreements and MoUs aimed at strengthening their defense ties.
This has included the signing of the India-US Defense Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI), which is aimed at promoting joint defense research and development, and the exchange of military personnel for training and education purposes.
India and the United States have also engaged in joint military exercises and training programs, which have helped to enhance the operational readiness and capabilities of their armed forces. The two countries have also cooperated on regional security issues, such as counterterrorism, and have worked together to address regional security challenges, such as piracy, illegal arms trafficking, and extremism.
Overall, India-US defense ties and cooperation are an important aspect of the broader relationship between the two countries and are seen as critical to promoting regional stability, addressing common security challenges, and advancing shared strategic interests.
India’s relations with neighboring countries (e.g. Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka)

India has a complex set of relationships with its neighboring countries, including Nepal, Bhutan, and Sri Lanka. These relationships are shaped by a range of historical, cultural, economic, and political factors, and can be both cooperative and competitive.
India’s relationship with Nepal is one of its closest and most complex relationships with a neighboring country. The two countries share a long and porous border, a deep cultural connection, and a rich history of political and economic interaction.
India and Nepal have close military and security ties and cooperate on a range of issues, including counter-terrorism, trade and investment, and energy security. However, the relationship is also sometimes marked by tensions, particularly over border issues, trade imbalances, and India’s perceived interference in Nepalese politics.
India’s relationship with Bhutan is characterized by a unique “special relationship”, in which India provides significant economic and security assistance to Bhutan, in exchange for Bhutan’s close cooperation on regional security issues.
The relationship is seen as positive by both countries and has helped to maintain stability and security in the region.
India’s relationship with Sri Lanka has been complex and often fraught, particularly in the aftermath of the Sri Lankan civil war and the humanitarian crisis that accompanied it. India has been working to improve its relationship with Sri Lanka in recent years and has been actively engaged in supporting Sri Lanka’s economic and political development.
India has also played a role in supporting Sri Lanka’s efforts to address the legacy of the civil war and promote reconciliation and healing among different ethnic and religious communities.
Overall, India’s relationships with its neighboring countries are a critical aspect of its foreign policy and regional strategy and are seen as crucial to promoting stability and security in the region. India seeks to maintain close and cooperative relationships with its neighbors, while also addressing any areas of concern and competition responsibly and constructively.\
India’s nuclear policy and stance on non-proliferation

India has a long-standing commitment to nuclear disarmament and the non-proliferation of nuclear weapons. India has maintained a “no first use” policy concerning its nuclear weapons and has repeatedly emphasized the importance of reducing the risk of nuclear weapons use and promoting global disarmament.
India has also been a strong advocate of the need to maintain the stability of the global nuclear order and has supported the strengthening of the global non-proliferation regime. India has signed and ratified the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) and is a member of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
However, India’s nuclear policy has been shaped by its unique security challenges and strategic interests. India has a declared nuclear deterrent, which it regards as essential to its national security, and it has developed nuclear-powered submarines and other strategic delivery systems.
India has also been a leading advocate of the need to create a more equitable and inclusive global nuclear order and has been critical of the current NPT regime, which it sees as discriminatory.
India has also played an active role in promoting regional and global stability, including through its support for disarmament initiatives and its participation in international forums focused on non-proliferation and disarmament.
India has also been actively engaged in global efforts to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Overall, India’s nuclear policy and stance on non-proliferation are shaped by its strategic interests and security challenges, as well as its commitment to promoting global stability and reducing the risk of nuclear weapons use.
India seeks to maintain a credible nuclear deterrent, while also supporting efforts to reduce the role and importance of nuclear weapons in international affairs.
India’s space program and military applications of space technology

India has a well-developed space program, with the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) as the primary agency responsible for its development. The Indian space program has a strong focus on the peaceful use of space technology for various applications such as satellite-based remote sensing, satellite-based meteorology, satellite-based navigation, satellite-based telecommunications, and satellite-based weather forecasting.
In addition to these civilian applications, India has also been exploring the military use of space technology. This includes the development of military satellites, satellite-based surveillance systems, and satellite-based communication systems for the Indian armed forces.
However, the exact details of India’s military space program are not publicly available due to security concerns.
India’s stance on regional and global terrorism

India has a strong stance against terrorism, both regionally and globally. The country has been a victim of terrorism for many years and has taken strong measures to counter it both domestically and internationally.
India has called for international cooperation in combating terrorism and has been actively participating in regional and global forums to address the threat of terrorism. India has also been supporting the UN’s efforts to combat terrorism and has called for the adoption of comprehensive conventions to address the issue.
Additionally, India has been strengthening its domestic security measures to tackle terrorism, including increasing intelligence-gathering capabilities, improving border security, and launching targeted operations against terrorists.
India believes that terrorism poses a threat to global peace and security, and it is committed to working with the international community to eradicate this menace.
India-Russia defense and security cooperation
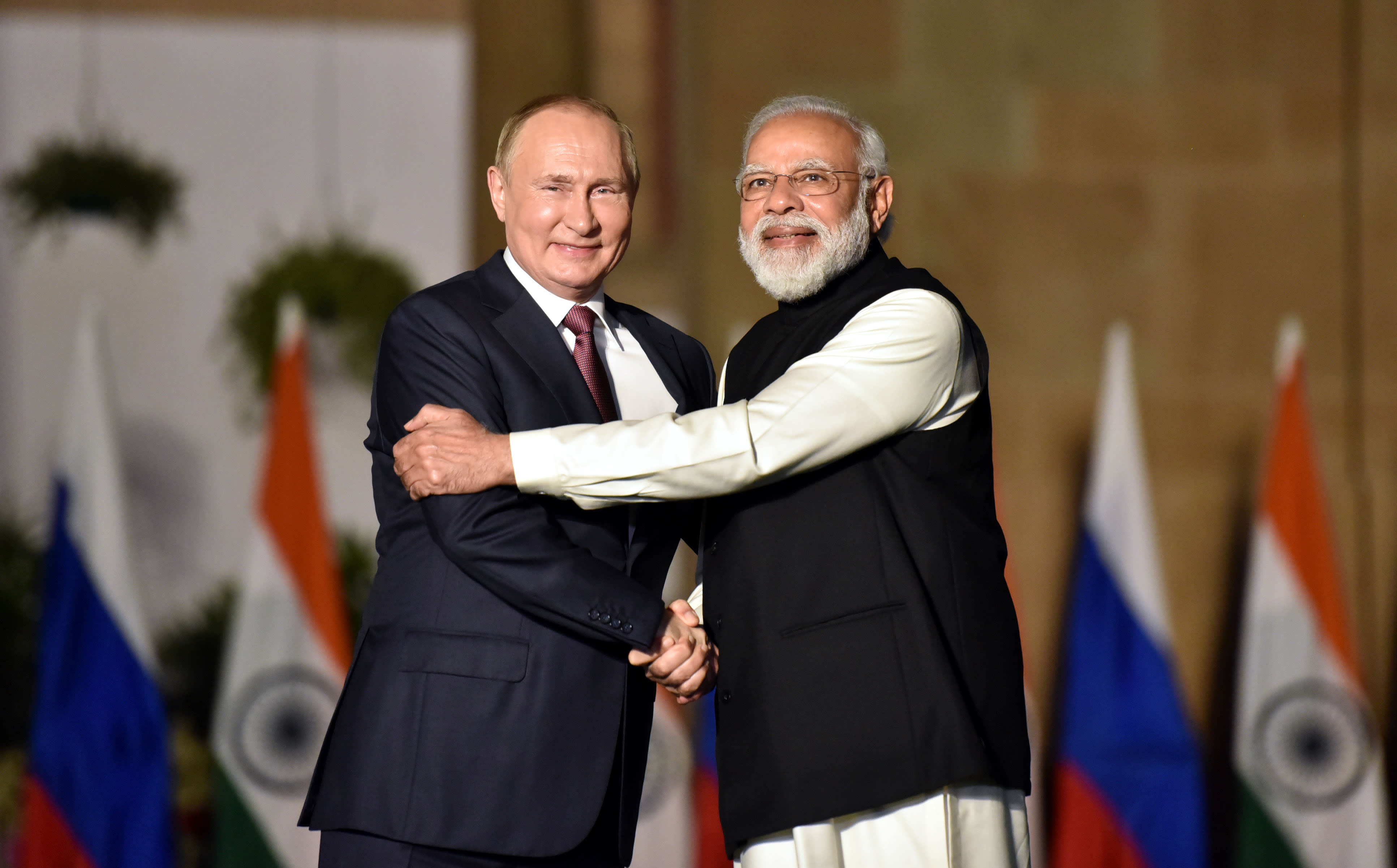

India and Russia have a long-standing and strong defense and security cooperation relationship. The two countries have been cooperating on various fronts, including the development and procurement of military equipment, joint military exercises, and intelligence-sharing.
India is one of the largest buyers of Russian military equipment, and the two countries have signed several agreements to enhance their defense and security cooperation.
In recent years, the two countries have been exploring new areas of cooperation, such as the development of advanced military technology and the joint production of defense equipment.
India and Russia also have close cooperation in the field of counterterrorism, with regular intelligence exchanges and joint exercises.
In addition to their defense and security cooperation, India and Russia also have strong political, economic, and cultural ties. The two countries hold regular high-level meetings to discuss ways to enhance their bilateral cooperation, and they have a common stance on several international issues, such as the fight against terrorism and the promotion of stability in the region.
Overall, India and Russia’s defense and security cooperation is a crucial pillar of their bilateral relationship, and it is expected to continue to strengthen in the coming years.
India’s role in regional and international organizations (e.g. BRICS, SAARC, UN)

India is an active member of several regional and international organizations, including:
BRICS: India is one of the five member countries of the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) group, which aims to promote economic cooperation and development among its member countries.
SAARC: India is a founding member of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), which is a regional organization aimed at promoting economic and cultural cooperation among South Asian countries.
UN: India is a founding member of the United Nations (UN) and is actively involved in various UN programs and initiatives, including peacekeeping operations, disaster relief, and sustainable development.
India has also been elected as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council several times and has been a strong voice in the UN on several global issues.
In addition to these organizations, India is also a member of several other regional and international organizations, including the World Trade Organization (WTO), the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the G-20.
India’s active participation in these organizations reflects its commitment to regional and global peace, security, and prosperity.
India’s economic and trade relations with other countries

India has diverse and dynamic economic and trade relations with many countries around the world. Some of the key countries with which India has strong economic and trade ties are:
United States: India and the US have a strong economic and trade relationship, with bilateral trade between the two countries reaching over $142 billion in 2021. The US is also a major source of foreign investment for India.
China: India and China are two of the largest economies in the world, and their trade relationship has been growing rapidly in recent years. However, there have been tensions between the two countries in recent times, particularly on the border issue.
Japan: India and Japan have a strong economic and trade relationship, with Japan being a major source of investment and technology for India. The two countries have also been working together on infrastructure projects in India.
European Union: India has a strong trade relationship with the European Union (EU), with bilateral trade between the two reaching over $140 billion in 2021. The EU is also a major source of foreign investment for India.
United Arab Emirates (UAE): India and the UAE have a strong economic and trade relationship, with the UAE being a major source of oil for India and a major market for Indian exports.
India is also actively engaged in regional and global trade initiatives, including the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). India’s strong economic and trade relationships with other countries reflect its growing role as a major player in the global economy.
India’s energy security and dependence on foreign sources of energy
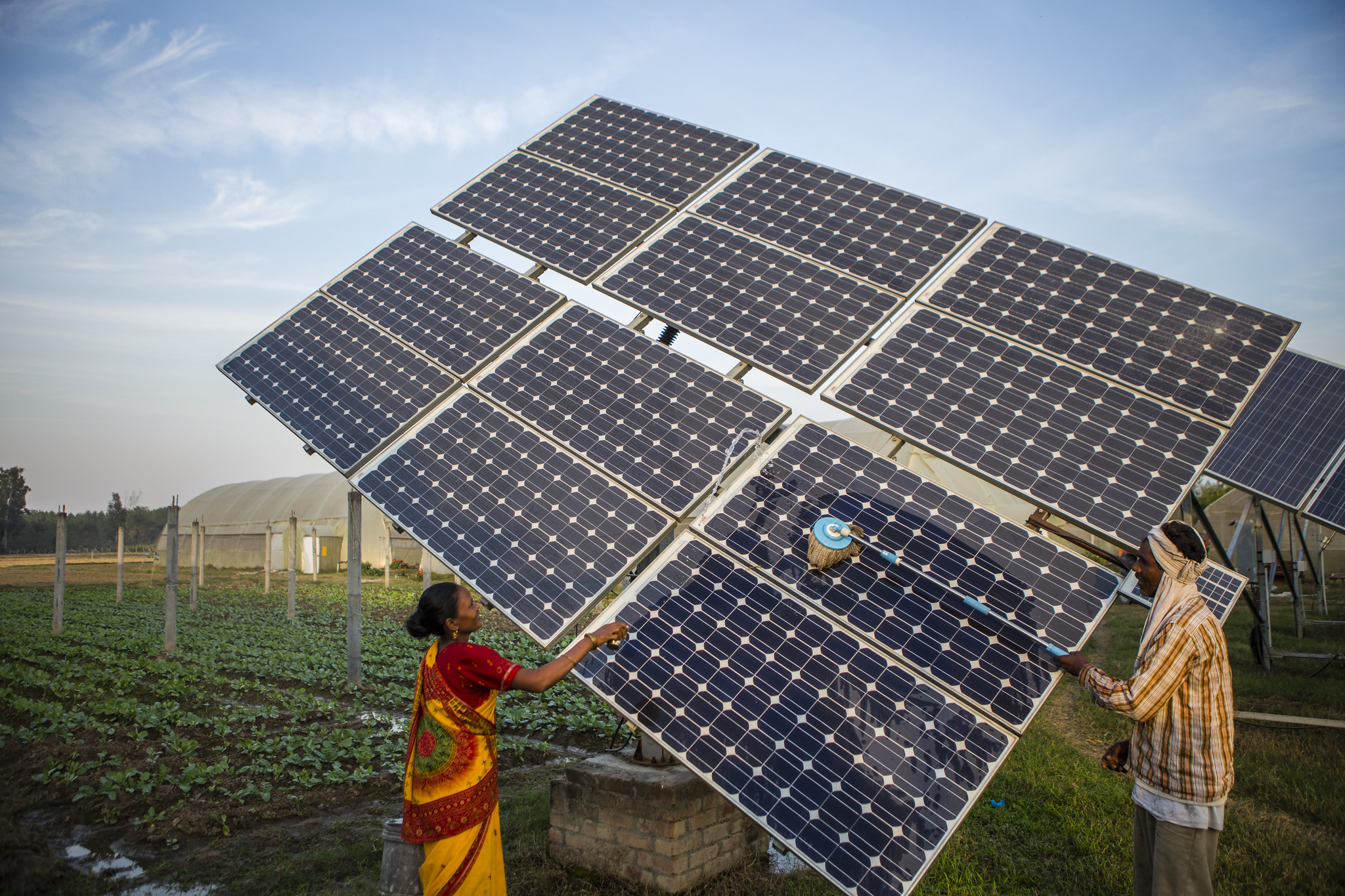

India is heavily dependent on foreign sources of energy to meet its growing energy needs. The country imports a significant portion of its crude oil, natural gas, and coal to meet its energy demand. This dependence on foreign sources of energy poses a challenge to India’s energy security, as fluctuations in global energy prices and supply disruptions can impact the country’s economy.
To address this challenge, India has been pursuing a multi-pronged strategy to enhance its energy security. This includes:
Diversifying its energy mix: India has been focusing on increasing the share of renewable energy in its energy mixes, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels.
Promoting energy efficiency: India has been implementing various measures to promote energy efficiencies, such as the use of energy-efficient appliances and the adoption of energy-efficient technologies in industry and transportation.
Developing domestic energy sources: India has been investing in the development of domestic energy sources, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, to reduce its dependence on imports.
Improving energy infrastructure: India has been investing in the improvement of its energy infrastructure, such as the expansion of its refining capacity and the development of natural gas pipelines, to enhance its energy security.
Despite these efforts, India’s dependence on foreign sources of energy is expected to remain high in the near term. However, the country is committed to reducing its dependence on imports over the long term and enhancing its energy security through a combination of domestic production and energy-efficient measures.
India’s cyber security policies and initiatives

India recognizes the importance of cyber security in the digital age and has taken several initiatives to enhance its cyber security posture. Some of the key policies and initiatives in this area are:
National Cyber Security Policy (2013): The National Cyber Security Policy outlines the government’s approach to securing India’s critical information infrastructure and promoting a secure and resilient cyberspace.
Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In): CERT-In is India’s national nodal agency responsible for responding to computer security incidents and providing technical assistance to individuals and organizations.
National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC): The NCIIPC is a government agency responsible for protecting India’s critical information infrastructure from cyber threats.
Digital India initiative: The Digital India initiative aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy. One of the key objectives of this initiative is to enhance the country’s cyber security posture.
Capacity building: India has been investing in the capacity building of its cyber security workforce, including the training of law enforcement agencies and the development of technical expertise in the private sector.
International cooperation: India has been actively engaging in international cooperation on cyber security, including the participation in regional and global forums, such as the Shanghai Cooperation Organization and the UN Group of Governmental Experts on Developments in the Field of Information and Telecommunications in the Context of International Security.
These policies and initiatives reflect India’s commitment to enhancing its cyber security posture and protecting its critical information infrastructure from cyber threats.
India’s maritime security and territorial disputes in the Indian Ocean region

India has a long coastline and a strategic location in the Indian Ocean region, making maritime security a key concern for the country. India has been actively working to enhance its maritime security and protect its territorial interests in the Indian Ocean region.
India has several territorial disputes in the Indian Ocean region, including those with neighboring countries over maritime boundaries and the exploitation of maritime resources. India has also been concerned about the increasing presence of foreign naval forces in the Indian Ocean region and the threat posed by piracy and illegal fishing.
To address these challenges, India has taken several initiatives to enhance its maritime security, including:
Building its naval capabilities: India has been investing in the modernization of its navy and the development of its coastal defense infrastructure, including the construction of new ports and the development of offshore energy installations.
Promoting regional cooperation: India has been actively engaged in regional cooperation on maritime security, including the participation in regional organizations, such as the Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC) and the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC).
Strengthening law enforcement: India has been working with regional partners to enhance its law enforcement capabilities, including the suppression of piracy, the prevention of illegal fishing, and the protection of maritime trade routes.
Managing territorial disputes: India has been pursuing diplomatic solutions to resolve its territorial disputes in the Indian Ocean region, including negotiations with neighboring countries and the use of international tribunals.
These initiatives reflect India’s commitment to enhancing its maritime security and protecting its territorial interests in the Indian Ocean region, which is critical to maintaining regional stability and ensuring the free flow of trade and commerce.
India’s human rights record and relationship with minority groups
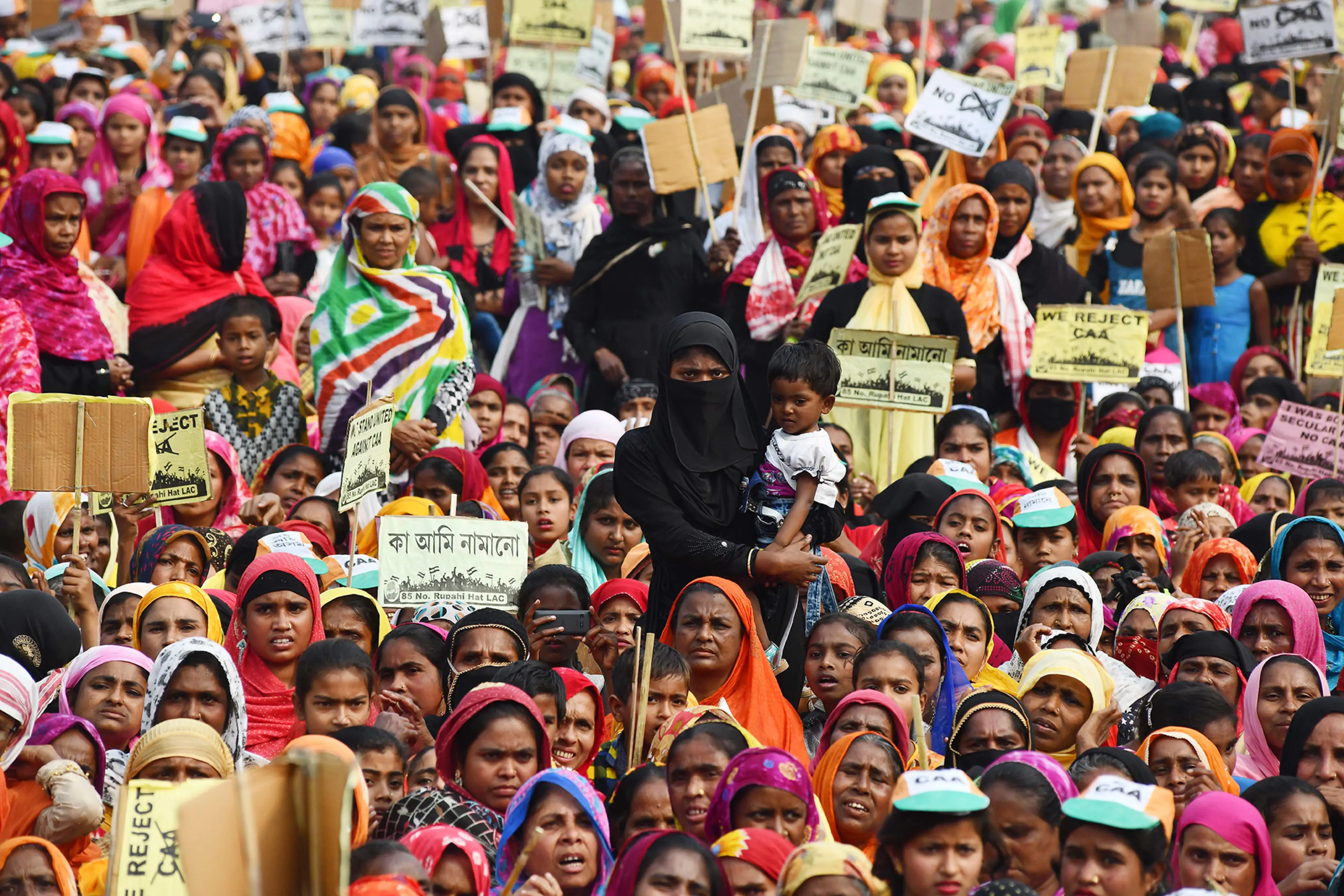

India is a diverse country with a large population of minority groups, and the protection of human rights and the rights of minority groups is an important issue in the country. However, there have been concerns about the treatment of minority groups in India, particularly in the areas of religious freedom, discrimination, and violence.
The government of India has taken several initiatives to protect the rights of minority groups, including:
Protection of religious freedom: India has a secular constitution that guarantees freedom of religion, and the government has taken steps to protect this right, including the implementation of laws to prohibit religious discrimination and the prosecution of individuals who engage in religious violence.
Promotion of equality: The government has taken steps to promote equality, including the implementation of affirmative action programs to improve the economic and social status of minority groups.
Addressing discrimination: India has implemented laws to address discrimination based on religion, caste, and gender, and the government has taken steps to enforce these laws, including the prosecution of individuals who engage in discriminatory practices.
Despite these efforts, there have been ongoing concerns about the treatment of minority groups in India, including allegations of violence, discrimination, and violations of religious freedom. The government has been working to address these concerns, including through investigations and the prosecution of individuals who engage in human rights abuses.
Overall, the protection of human rights and the rights of minority groups is an ongoing challenge in India, and the government has been working to address these issues through a combination of legal and policy measures.
India’s efforts to address climate change and environmental sustainability
India recognizes the importance of addressing climate change and promoting environmental sustainability and has taken several initiatives to address these challenges. Some of the key efforts in this area are:
Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs): India submitted its Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), outlining its commitment to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions intensity and increase its use of renewable energy.
National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): The National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) outlines India’s strategy for addressing climate change and promoting environmental sustainability, including the development of low-carbon and sustainable development pathways.
Renewable energy: India has taken several steps to increase its use of renewable energy, including the implementation of policies to support the development of wind, solar, and other forms of renewable energy, and the expansion of its grid infrastructure to accommodate the integration of renewable energy into the national grid.
Energy efficiency: India has taken steps to improve its energy efficiency, including the promotion of energy-efficient technologies and practices, and the implementation of energy-efficient building codes and standards.
Sustainable agriculture: India has been working to promote sustainable agriculture practices, including the promotion of organic and agro-forestry practices, and the implementation of policies to support the development of sustainable agricultural systems.
Environmental protection: India has implemented several laws and policies to protect its natural resources and biodiversity, including the protection of wildlife, forests, and water resources, and the management of hazardous waste.
These initiatives reflect India’s commitment to addressing climate change and promoting environmental sustainability, and the country continues to work with international partners to address these global challenges
India’s role in resolving regional conflicts and promoting peace and stability.

India has played a significant role in promoting peace and stability in the regional and international arena. Some of the key efforts in this area include:
Mediation and conflict resolution: India has a tradition of mediating and resolving regional conflicts through diplomacy and peaceful means, and has been involved in resolving several regional disputes, including between neighboring countries and within its borders.
Peacekeeping: India is one of the largest contributors to United Nations peacekeeping missions, and has been involved in peacekeeping operations in several regions around the world.
Diplomatic engagement: India has a robust diplomatic engagement with its neighbors and regional partners, and has been actively involved in promoting regional stability and security, including through the development of regional organizations such as the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC).
Conflict prevention: India has been working to prevent conflicts through diplomatic engagement and conflict resolution initiatives, and has been involved in efforts to promote peace and stability in regions such as the Korean Peninsula, the Middle East, and Africa.
Humanitarian assistance: India has been providing humanitarian assistance to countries affected by conflict and natural disasters, including through the deployment of its military and other assets, and the provision of financial and technical support.
Overall, India’s role in promoting peace and stability in the regional and international arena reflects its commitment to working with international partners to address global challenges and build a more secure and stable world.



