How does a startup get new funding? 16 types of startup funding and its stages.

How does a startup gets funding? 16 types of startup funding and its stages
The information era has seen a tremendous rise in new businesses. This trend continues today, and for those that succeed, starting a company may be a rewarding effort. This post will go over what a startup is, how it’s funded, and what stages it goes through.
There’s no uncertainty that launching a company is difficult and requires alot of funds. But don’t let it deter you from pursuing your main aim of creating your own company. Many people have beautiful ideas, but because they lack the financial resources to turn them into a business, they tend to leave them at just that. They do not understand that there are a variety of funding options available to assist them in making their ideas a reality.
Some entrepreneurs have the good fortune of financing the major part of their launch expenditures with their own money. However, not everyone has sufficient personal funds. Even wealthy startups often require investment from incubators or accelerators. When you don’t have enough money to establish your firm, you may choose between two forms of financing: Equity Financing and Debt Financing.
Both of these funding methods differ in many ways, but they both result in funds for your company’s expansion.
But what is a startup ?
A startup is a business in its early phases of development. One or more entrepreneurs create a company to meet a specific need for a product or service. Startups are high-cost, low-revenue enterprises, forcing them to seek outside funding before turning a profit.
What is the process for getting startup funding?
Individuals or groups use startup funds to raise funding for their new firm, allowing it to flourish. When investors contribute to the financing of a startup, they do so in the hopes of receiving a more important sum of money from the company in the future. Depending on how much money a person has put in a company, they may make business decisions that affect how it functions.
Money is crucial to remodel a brilliant idea into a fantastic business, but “Money does not grow on trees,” as the saying goes, and you may not have thousands of dollars on hand. So, how can you make your dream a reality? Here are a few of the best alternatives.
With countless tech companies going public and roughly 42 companies becoming unicorns in 2021, India’s startup ecosystem has gone a long way. In 2021, Indian entrepreneurs raised $42 billion in capital over 1,583 contracts, according to Inc42’s Indian Tech Startup Fundraising Report 2021, and 2,487 distinct investors engaged in startup funding. Software-as-a-service (SaaS), eCommerce, banking, and consumer services have all received a lot of money.
Between 2014 and the end of January 2022, Indian companies raised about $116 billion in investment.
If you’re looking for money, keep in mind that bankers do not recognize themselves being the traditional source of capital for enterprises. And if you come to them for the first time seeking finances without first exploring other options, there is a chance of them viewing it negatively. As a result, it is critical to be proactive in getting money for your company.
It doesn’t matter where you got your money from at the end of the day. Each funding source has its own set of benefits and drawbacks, implying that none of them is perfect. Aside from that, the requirements for your firm should be considered while asking for funding.
Bootstrapping is the first step. You’ll need money for operations, growth, marketing, and manufacturing for expansion of the company. You seek seed investment from angel investors, then Venture Capitalists, and finally an Initial Public Offering, depending on the stage of your firm and its potential to create profits (IPO).

The three types of startup financing available are Equity, Debt, and government subsidies. Each funding option has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. For Example, Equity Finance has no repayment conditions but does demand you to give up a stake in your company, making it the most expensive type of financing.
The startup funding ecosystem has extended beyond angel investors and Venture Capitalists. Depending on their needs and stage, startups can raise funds from multiple investors and platforms. We’ll go through 16 startup funding alternatives in this post.
- Self-Funding / Bootstrapping
Many entrepreneurs start by Self-Funding (known by the term Bootstrapping), and investors will want to see that you have some “skin in the game.” Even if you can only contribute a tiny amount of money, it is worthwhile to evaluate the benefits. For example, you won’t have to worry about keeping investors happy. You can keep a more important part of the revenues for yourself.
Many entrepreneurs in addition refuse to take a salary, preferring to put their money in a 401(k) retirement plan or working a part-time job to supplement their income while growing their business.
Instead of relying on future investment rounds, you may use your first revenues to bootstrap future growth.
- Friends and Family Investors
Your friends and relatives may be keen to assist you in your development, but they are unlikely to make you jump through the many hoops. These investments are often loans or stock purchases, and they are something that later investors would possible view to be a positive (i.e., why should the Investor Trust in you if your family and friends don’t?).
To protect yourself and your contacts, make sure you have an definite written agreement that explains how the money will be reimbursed. Also, even if the agreement is informal, you should check to see for any securities limitations in place.
- Angel Investors
Individuals who invest in tiny enterprises are known by the term Angel Investors.
Angel investors are individuals or groups of individuals with familial ties or considerable knowledge. The majority of them has experienced business entrepreneurs who have gone through the startup phase. They are aware of the issues in addition to the opportunities.
These are cash-rich investors who are ready to put their money into your startup at the early stage. They evaluate the startup, conduct research, and determine how much the entrepreneur has invested before investing. Once they are convinced, they provide money in exchange for convertible debt or Equity in the company.
Angel investors serves like a mentor for young entrepreneurs. They spend less and expect higher returns than Venture Capitalists. Individual investors like Kunal Shah, Rajan Anandan, and Ritesh Malik are well-known.
- Angel Networks & Platforms
Through angel networks and platforms, angel investors combine their funds to invest in enterprises. Because they function like a group, these investors may provide more substantial amount and control risks. The platform is provided with equity in the company and is rewarded if it succeeds.
AngelList, Venture Catalysts, and LetsVenture are the most prominent sites.
- Venture Capital Funds
A Venture Capital fund is a financial entity that invests in potential startups. This is when a company’s funding progresses to the following stage Venture Capital firms invest huge quantities of money in a company’s development and expansion while closely monitoring its progress to ensure that their investment creates long-term growth.
In return for financing, Venture Capital funds get shares or equity-linked securities from entrepreneurs. They leave when the company goes public or is bought.
- Micro Venture Capitalists (Micro VCs)
Micro VCs are Venture Capital firms with funds ranging from $60 million to $70 million. In return for a piece of the company’s equity, micro VCs invest in early-stage companies.
- Corporate Venture Capital
Corporate Venture Capital(CVC) is another type of VC. CVCs are giant multinational corporations that invest corporate capital in young, creative startups for a lot of reasons, including technology, talent pool, and market acquisition.
CVCs give resources like marketing skills, strategic guidance, or a line of credit to businesses. Being in touch with well-known brands will help a company get traction.
CVC provides capital in return for a share of the company’s stock. Mahindra Partners, Reliance Ventures, and Times Group’s Brand Capital are Indian CVCs.
- Venture Debt Funds
For entrepreneurs, equity is a expensive form of finance. As a result, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) provide debt funding to VC-backed firms under a hybrid scheme known by the term venture debt funds. When a business grows and requires working money, bank loans or stock are not viable options.
Venture debt funds provide you money in return for non-convertible debentures (NCDs) and Equity Warrants. Some companies that provide venture loan financing to Indian businesses are Alteria Capital and Trifecta Capital.
- Government Grants & Funds
When the Indian government established the ‘Startup India‘ Initiative in 2016, funding for Indian businesses extended beyond angel investors and Venture Capitalists. Startups who register for the program are eligible for subsidies like an 80% discount on clear expenses and a three-year income tax exemption.
The government disburses the funds like loans through the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) Fund of Money Scheme. The fund invests in Venture Capital and Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) in early-stage companies. Last year, the government launched the Startup India Seed Fund, which provides financial help to initial phase startups.
For the current fiscal year, the government has earmarked INR 1,000 crore for the Startup Fund of Funds and INR 283.5 crore for the Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS).
- Accelerators & Incubators
Incubators and accelerators are analogous to startup prep schools, but all of the funding, like mentioned above, options are for already-existing enterprises. These programs run for four to eight months and give entrepreneurs money and a place to meet investors, mentors, and other entities.
In most cases, accelerators and incubators are located in big cities and need an ownership investment in return for their services. Individual entities, big enterprises, or big tech companies charge these programs.
Y Combinator, GSF Accelerator, Microsoft Accelerator, Google Launchpad Accelerator, and JioGenNext are just a few famous accelerator programmes for Indian entrepreneurs.
- Family Offices
Family Offices are another source of investment for Indian entrepreneurs. In India, family enterprises have a long tradition of transfering their fortune to the next generation. Wipro’s Azim Premji, K. Damani Group’s Anirudh Damani, and Burman Family Office’s Gaurav Burman are all examples (investor in Dabur India). This generation aspires to defy stereotypes and invest in a variety of Ventures.
Angel investors are impatient, but Family Offices are patient. They allow companies to expand their entities with more time, money, and resources. But getting in touch with the right family office is the key.
About 140 Family Offices in India have made substantial investments in the startup ecosystem. According to a research by Praxis Global Alliance and 256 Network, they have been actively participating in 50+ such agreements every year since 2015.
Indian Family Offices are predicted to contribute 30% of the estimated $100 billion raised by Indian entrepreneurs by 2025.
- Banks
Despite all of the new funding sources available to Indian companies, bank loans continue to be a viable choice. Diversing sorts of loans, like equipment loans, starting company loans, and working capital loans, are available from banks, each with different conditions. There is a loan accessible for every step of a company’s development.
Banks often want more collateral for an idea-stage entity, usually in the form of other sources of revenue. Fullerton India and Omozing.com are two well-known banks and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) that provide loans to Indian entrepreneurs.
- Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding is another less common startup funding alternative. Several retail investors seeking alternative investment opportunities gather on a platform, evaluate the business plan, and invest in the startup of their choosing. Every investor puts a predetermined amount of money into a business concept in the hopes of earning a bigger return (peer-to-peer lending).
Equity Crowdfunding is another option, although its legality in India is debatable. Scams and disputes abound in the world of crowdfunding. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has issued a warning against unregistered digital crowdfunding sites.
Indiegogo, SeedInvest Technology, Mightycause, StartEngine, GoFundMe, Patreon, GripInvest, and ImpactGuru are some of the most well-known crowdfunding sites for entrepreneurs.
- Revenue Based Financing
Revenue-based financing enables a business to receive its future revenues in advance, that may then be used to fund inventory, advertising, and marketing. The payment section is alterable, consisting of a pre-determined share of a company’s monthly sales. In recent years, India has seen the emergence of many revenue-based lending organisations that cater to businesses’ revenue demands.
Velocity, Klub, and GetVantage are just a few of the revenue-based funding businesses for Indian entrepreneurs.
- Partnership / Licensing
Growing on your own isn’t always the best option. Instead, form a Partnership or licence agreement with a well-established entity that may profit from your product.
For example, if you invented a cell phone battery that lasted twice in comparison to existing batteries, you could either try to market your battery independently to consumers, which would be expensive and risky, or (ii) strike a Licencing Deal with an established manufacturer who would love to include your battery in their next model, which would be lucrative.
In a Partnership or licence Agreement, cash may be confined to a first-order advance to assist you in scaling up your production. The greater benefit is that you will need less cash because you’ll save money on putting up your own Supply Chain and marketing plan.

- Commitment to A Major Customer
If you can get a big customer on board, they could be willing to help fund your development. In return, they may want that your production process be tailored to their exact specifications, that exclusive distribution rights be granted, or that specialised assistance be provided. This promise might be related to a pre-licensing agreement or a white-label transaction.
You’ll also benefit from the security of a guaranteed minimum return, which lowers the risk of your investment.
You can’t just start a firm out of thin air if you have a billion-dollar concept. You’d need an office, a website, workers, and a slew of other necessities. And you’ll need money to do it. Every business requires at least a small sum of money to get off the ground, and you may want more with the growth of the firm.
However, before we can discuss the later stages, we must first understand the business’s Initial investment. Seed money is the term for the Initial investment. It is the Initial investment for every firm, and it is utilized to launch and expand the business. This is usually a little sum that may be gained by issuing a share of the company’s ownership.
Seed investment can help your firm grow into a major corporation in the future, because seed capital just serves like a stepping stone to a profitable business. Furthermore, startups always expand after receiving Initial capital, eventually expanding into large corporations. Overall, seed capital aids in the growth of a firm and its transition into the real world. This is why it is the most crucial of all financial options.

The 8 Stages of Funding a Startup
The following are the steps of obtaining funding for a startup:
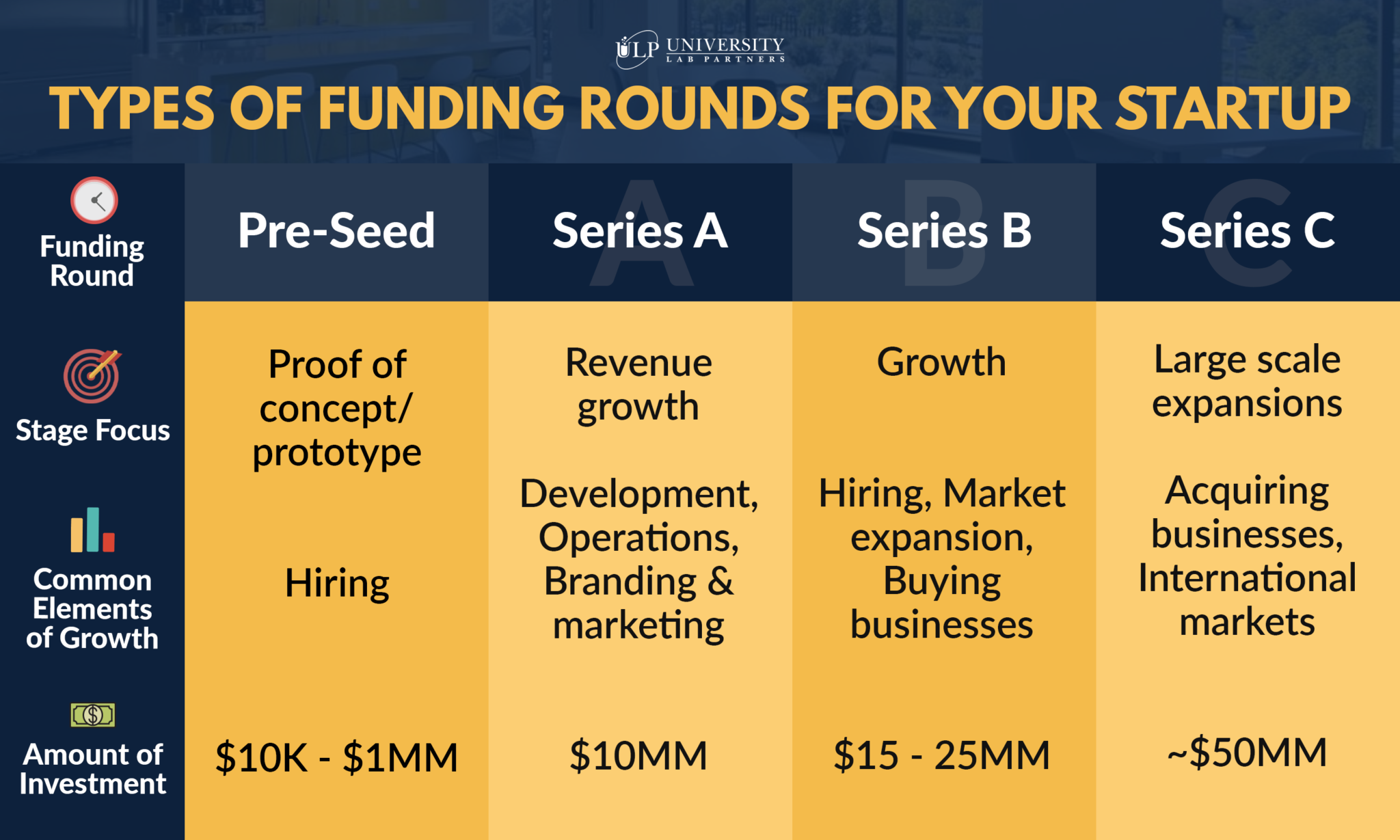
Pre-seed funding stage
This is the research stage of starting a business. Make sure you answer the following questions at the pre-seed stage:
-Is your idea feasible?
-Is it possible that your idea has already been implemented?
-How much does your business cost?
-What business model would you employ?
-How are you going to get started?
In many cases, you or your friends and family provide the majority of the business finance during this stage. In this stage, the overall worth of a business might range from $10,000 to $100,000.
Seed funding stage
At this point, your concept has developed into a viable business with some momentum among customers. In this phase, entrepreneurs give up firm stock to increase sums of money from investors. The following expenses are paid by seed funding:
-Launch of a New Product
-Product promotion
-New employees
-Product-market-fit market research
This level of capital raising is open to startups with a valuation of $100,000 million to $6 million.
Series A funding
The Series A fundraising stage signals the start of Venture Capitalist involvement, with the company’s shares being given in return for funds.
You may start preparing yourself for future business development at this time. The following are examples of this:
-Increasing the efficiency of your company
-Financial losses or deficiencies must be compensated for
-Developing your product or service further
-Developing a development strategy that is scalable
Series B funding
Startups at this level have loyal user bases and consistent income sources. You’ve proved that you can scale your concept at this point. Investors can now assist you in the following ways:
-Use innovative market-reach strategies.
-Boost your market share
-Assemble operational teams, include those in charge of company development and marketing.
Series C funding
Series C investment is for a firm that is progressed on its way to success and is looking to extend its operations globally. Investors may be more willing to invest at this stage if they believe the firm will prosper. During this phase, funds are utilized for the following:
-Create new goods
-Expand your market.
-Invest in under-performing companies in the same field.
Series D funding and beyond
A business often continues beyond the Series C fundraising round for two reasons. They are as follows:
New opportunities: A potentially profitable possibility arises that necessitates the company’s activity prior to the IPO (IPO).
Poor performance: The firm fails to meet the aims stated during the Series C fundraising round. The company subsequently raises more money in a Series D round to solve the problems.
A startup can go through with many investment rounds it wants. If a company’s revenue targets are advanced, it may complete many fundraising series, it needs.
Bridge loans and mezzanine financing
These loans are intended for entities with a market value of at least $100 million. For lenders, a mezzanine loan is a blend of debt and equity, while bridge loans are used for short-term funding. They bridge the financial gap between this stage and the first Public Offering. The money is probable to be used to buy out a company’s management or acquire a rival. Loans usually last six to twelve months and are repaid with IPO profits.
IPO
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the final stage of startup success. It occurs when the company’s shares are first made available for public purchase. The IPO is utilized to raise funding for further expansion or to allow the founders of the company to sell out their remaining shares for personal gain.
During the process of getting ready for an IPO, substantial events occur. They are as follows:
Putting together a team of SEC Specialists, Attorneys, accountants, and underwriters to help with the Public Offering.
Compilation of startup data, including financials and projected future operations
An audit of the company’s financial accounts is being conducted.
Completion of the Governmental IPO requirements, which include submitting the starting prospectus with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and confirming the Offering date.
The ideal funding solution is ultimately a personal choice based on your particular objectives and risk tolerance. Consulting with an experienced business lawyer who has seen many entities thrive and fail can assist you in making the best option for you.
Because of the multiple funding choices accessible to entrepreneurs, India has risen to become the world’s third-largest startup ecosystem. The main aim of these finance and fundraising tools is to help businesses expand.
Finding money is well-known to be hard, yet it is necessary to get your company concept off the ground. And it is the most wonderful thing in the world when your firm starts to work and becomes self-sustaining. After all the work of safeguarding one of the types of finance, you’d be on your way to success and wouldn’t need any outside funds.
That’s when you know you’ve taken the proper steps to turn your dream business become a reality.
edited and proofread by nikita sharma




