Incorporate A Company In Slovenia In 2025

Slovenia, a small yet enchanting country in Central Europe, is known for its breathtaking landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and strategic location. Bordered by Austria, Italy, Croatia, and Hungary, it acts as a gateway between Western Europe and the Balkans. A member of the European Union (EU), Schengen Area, and Eurozone, Slovenia enjoys strong economic ties and progressive development.
Standard of Living in Slovenia
The country boasts a high standard of living, consistently ranking among the top nations in global human development indices. The country offers its citizens excellent healthcare, quality education, and robust social welfare programs. With a per capita GDP of approximately €27,000 and low unemployment rates, Slovenia provides economic stability to its population. The cost of living is moderate compared to other EU nations, making it an attractive destination for expats. Residents enjoy well-maintained public infrastructure, efficient transportation systems, and a safe environment.
Personal Taxes in Slovenia
Slovenia follows a progressive tax system for individuals, where tax rates increase with income. Residents are taxed on their worldwide income, while non-residents pay taxes only on income earned within Slovenia.
Income Tax Rates (2024):
- Up to €8,755: 16%
- €8,755 to €25,750: 26%
- €25,750 to €51,500: 33%
- Above €51,500: 50%
Additional taxes may apply, such as a solidarity surcharge for high-income earners. Social security contributions are also mandatory and are shared between employers and employees. These contributions fund healthcare, pensions, and unemployment benefits.
Despite relatively high tax rates, Slovenes benefit from a well-functioning public sector, including free or heavily subsidised healthcare and education.
Corporate Taxes in Slovenia
The country offers a favourable environment for businesses with its competitive tax rates and pro-business policies. The corporate income tax rate stands at 19%, making it one of the lower rates in the EU. Companies are taxed on their worldwide income, with foreign income eligible for relief under double taxation treaties.
Key Features of Corporate Taxation:
- Tax Incentives: The country provides incentives for investments in research and development (R&D), environmental protection, and employment generation.
- VAT: A standard VAT rate of 22% applies to most goods and services, while a reduced rate of 9.5% is applicable to essential items like food, books, and medicines.
- Withholding Taxes: Dividends, interest, and royalties paid to non-residents are subject to a withholding tax of 15%, unless reduced by double taxation agreements.
Major Industries in Slovenia
Slovenia’s economy is diverse, with several industries playing key roles in its development. These include:
- Manufacturing and Automotive Industry: Slovenia’s manufacturing sector is robust, producing a variety of goods, from machinery to consumer products. The automotive industry, in particular, is a major driver, with Slovenia serving as a hub for producing car parts and components for global brands like Renault and Volkswagen.
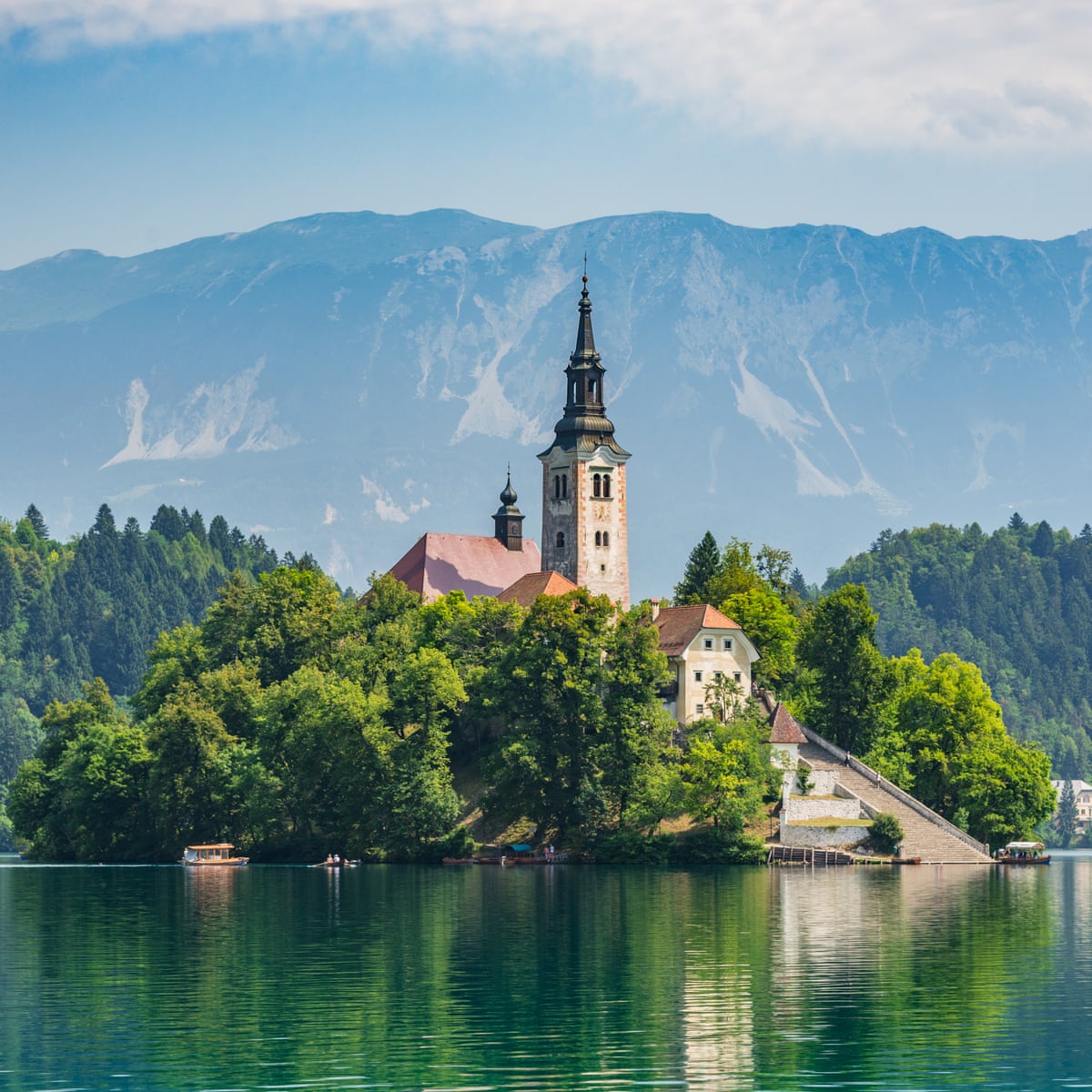
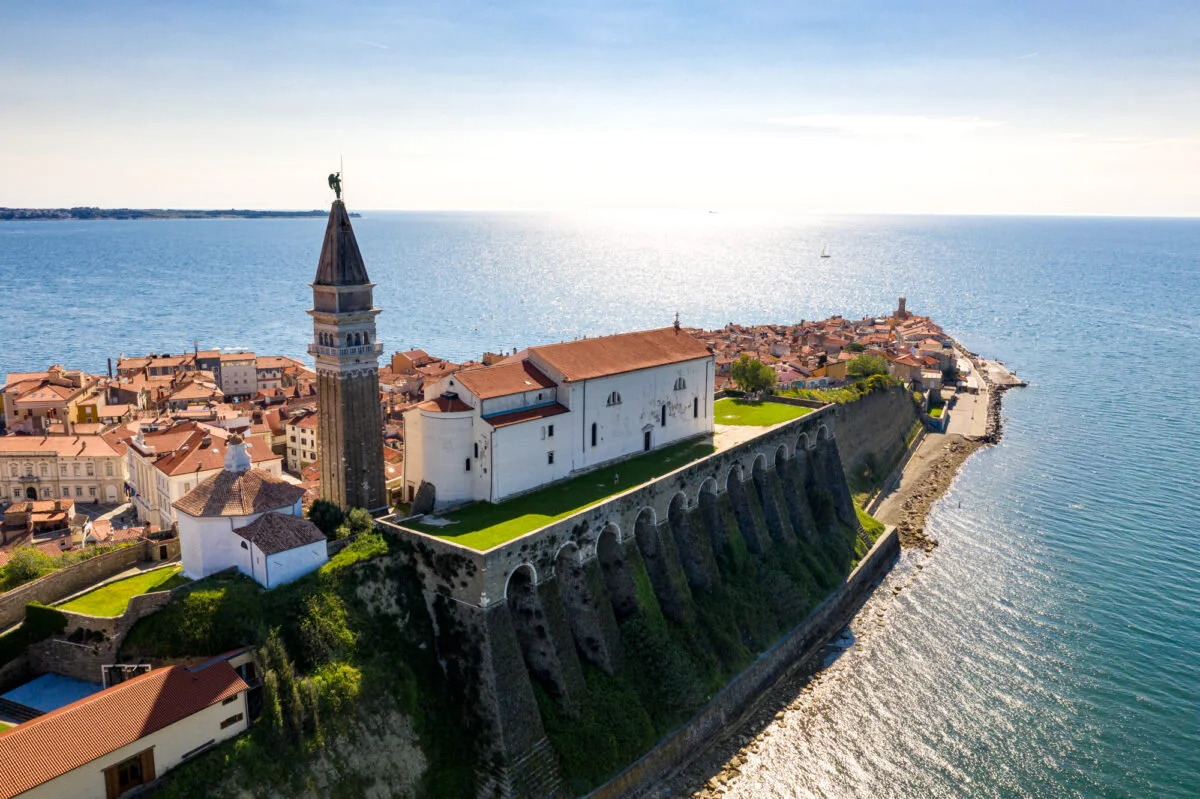
- Tourism and Hospitality: With its stunning natural landscapes, including Lake Bled, Triglav National Park, and the Adriatic coastline, Slovenia is a popular tourist destination. The sector contributes significantly to the economy, drawing millions of visitors annually.
- Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology: The country is a leader in pharmaceutical production in the region, with companies like Krka and Lek (part of Novartis) exporting medicines and biotechnological products worldwide.
- Green Energy and Environmental Technologies: Emphasising sustainability, Slovenia is investing in renewable energy sources, including solar, hydro, and wind power. The government actively supports initiatives promoting environmental conservation.
- ICT and Technology: The information and communications technology (ICT) sector is expanding, with startups and established companies innovating in software development, AI, and data analytics.
- Agriculture and Food Processing: The country is known for its wine production, honey, and high-quality dairy products. The agricultural sector remains vital to rural areas, while food processing industries cater to both domestic and international markets.
Inflation and Cost of Living in Slovenia
The country has maintained a relatively stable economy, with inflation rates fluctuating but generally lower than many other European nations. However, global economic pressures have led to rising living costs in recent years.
Cost of Living Overview:
- Housing: Rental costs vary significantly by location. In Ljubljana, the capital, a one-bedroom apartment in the city centre costs around €800–€1,200 per month, while smaller towns offer more affordable options.
- Groceries and Dining: Basic groceries are moderately priced, while dining out at mid-range restaurants typically costs €10–€20 per person.
- Utilities and Transportation: Monthly utilities average around €150–€200, and public transportation is reliable and affordable.
While Slovenia’s cost of living is higher than in some Eastern European countries, it remains more affordable than in Western Europe, making it an attractive option for expats.

Property Tax, Services Tax, and Sales Tax in Slovenia
Slovenia has a straightforward tax system that includes property taxes, sales taxes, and other levies:
- Property Tax: Property tax in the country is levied based on the value and use of the property. Rates are relatively low compared to other EU countries. Residential properties attract a lower tax rate than commercial or industrial properties. Property owners must also pay a transfer tax of 2% when selling real estate.
- Value-Added Tax (VAT): Slovenia applies a standard VAT rate of 22% on most goods and services. Essential items such as food, books, and medicines are taxed at a reduced rate of 9.5%. VAT compliance is critical for businesses operating in the country.
- Service Taxes: Businesses in specific sectors, like hospitality or telecommunications, may be subject to additional service-specific levies.
Types of Business Entities in Slovenia
Entrepreneurs looking to establish a business in the country have several options for structuring their company. Common business entities include:
- Limited Liability Company (Druzba z Omejeno Odgovornostjo – D.O.O.):
- Ideal for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Requires a minimum share capital of €7,500.
- Liability is limited to the capital invested.
- Public Limited Company (Delniska Družba – D.D.):
- Suitable for larger enterprises.
- Requires a minimum share capital of €25,000.
- Shares can be publicly traded.
- Sole Proprietorship (Samostojni Podjetnik – S.P.):
- Ideal for freelancers and small-scale operations.
- Easy to set up with minimal requirements.
- Owners have unlimited liability.
- Branch Office:
- Allows foreign companies to operate directly in Slovenia.
- Must register with local authorities.
Licenses to Start a Business in Slovenia
Starting a business in the country requires obtaining the necessary permits and licenses. Key steps include:
- Business Registration: Register the business entity with the Slovenian Business Register (AJPES). This process involves submitting required documents, including articles of incorporation and shareholder details.
- Tax Registration: Obtain a tax identification number from the Financial Administration of the Republic of Slovenia (FURS).
- Sector-Specific Licenses: Certain industries, such as food services, construction, and healthcare, require additional permits from relevant authorities.
- Municipal Approvals: Businesses must secure local municipality licenses, especially for physical establishments.
Opportunities for Expats for Business Growth in Slovenia
Slovenia’s open economy and EU membership create opportunities for expats looking to start or expand their businesses. Promising sectors include:
- Tourism and Eco-Tourism: The country’s commitment to sustainability makes it ideal for eco-tourism ventures and boutique hospitality businesses.
- Technology and Startups: The government actively supports ICT startups through grants and incubator programs. Ljubljana has a growing tech hub attracting global talent.
- Agriculture and Organic Products: With a focus on organic farming and sustainable agriculture, there’s room for innovation in food production and exports.
- Green Energy Solutions: Investments in renewable energy and environmental technologies align with Slovenia’s eco-friendly policies.
Citizenship for Expats in Slovenia
Slovenia offers pathways to citizenship for expats, though the process requires time and adherence to legal criteria:
- Residency Requirements: Expats must reside in the country for at least 10 years, with at least five years of continuous residence before applying for citizenship. Shorter residency periods may apply for individuals married to Slovenian citizens or those of Slovenian descent.
- Language Proficiency: Applicants must demonstrate proficiency in the Slovenian language, typically through a standardised exam.
- Naturalisation Process: The application is submitted to the Ministry of Interior and includes documents such as proof of residency, language proficiency, and financial stability.
- Dual Citizenship: The country allows dual citizenship only in certain cases, such as for those with Slovenian ancestry or under international agreements.

Why Register a Company in Slovenia?
Registering a company in Slovenia provides several benefits, making it an appealing choice for entrepreneurs:
- Strategic Location: Situated at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, Slovenia offers excellent connectivity to key European markets, including Austria, Italy, Hungary, and Croatia. Its infrastructure supports efficient trade and logistics.
- EU Membership: As a member of the European Union, Slovenia provides businesses with access to the EU’s single market, facilitating trade, investment, and mobility. Businesses registered in Slovenia enjoy harmonised regulations and opportunities to operate across member states.
- Stable Economy: Slovenia’s economy is stable, supported by a skilled workforce, strong institutions, and a favourable business environment. Key industries, such as manufacturing, tourism, and technology, provide growth potential for investors.
- Business Incentives: The Slovenian government offers tax incentives for investments in research and development (R&D), green energy, and employment creation. The country also has a competitive corporate tax rate compared to other EU nations.
- Ease of Doing Business: The country ranks highly for ease of starting and operating a business, with streamlined procedures and digitalised systems for company registration and administration.
How to Register a Company in Slovenia
The process of registering a company in the country is straightforward, supported by efficient administrative systems. Here are the key steps:
- Choose the Business Structure: Decide on the type of legal entity you wish to establish. Common structures include:
- Limited Liability Company (D.O.O.): Suitable for small and medium enterprises.
- Public Limited Company (D.D.): Ideal for larger enterprises.
- Sole Proprietorship (S.P.): Best for freelancers and small-scale operators.
- Branch Office: For foreign companies looking to operate in Slovenia.
- Reserve a Business Name: Select a unique name for your business and register it with the Slovenian Business Register (AJPES).
- Prepare Documentation: Draft and notarize the articles of incorporation, which outline the company’s purpose, share capital, and governance structure. You will also need identification documents for shareholders and directors.
- Register with the Slovenian Business Register (AJPES): Submit the required documentation to AJPES. This step officially establishes your company and assigns it a registration number.
- Obtain a Tax Identification Number (TIN): Register your company with the Financial Administration of the Republic of Slovenia (FURS) to obtain a TIN, which is essential for tax compliance.
- Open a Bank Account: Set up a corporate bank account in Slovenia and deposit the minimum share capital required for your chosen business structure.
- Obtain Additional Permits: Depending on the industry, you may need specific permits or licenses, such as those for food services, healthcare, or construction.
- Register for VAT (if applicable): If your business exceeds the VAT registration threshold or operates in certain sectors, you must register for VAT with FURS.
Cost to Register a Business in Slovenia
The costs of registering a business in Slovenia vary depending on the type of entity and associated administrative fees. Typical expenses include:
- Business Registration Fees: Registration with AJPES is free for sole proprietors and costs approximately €100–€200 for companies.
- Notary Fees: Notarization of incorporation documents costs around €150–€300, depending on the complexity of the documents.
- Minimum Share Capital:
- Limited Liability Company (D.O.O.): €7,500.
- Public Limited Company (D.D.): €25,000.
- Professional Services: Engaging a lawyer or business consultant for assistance with registration and compliance may cost €500–€1,000.
- VAT Registration (if applicable): No direct fees are charged for VAT registration, but compliance costs, such as accounting services, should be considered.

Relation with Other Countries of Slovenia
Slovenia’s foreign relations and trade partnerships significantly enhance its business environment. Key aspects include:
- European Union Membership: As an EU member, the country enjoys access to a single market of over 400 million consumers. This facilitates trade and investment across Europe.
- Regional Cooperation: The country is part of several regional initiatives, including the Adriatic-Ionian Initiative and the Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA), which promote economic cooperation.
- Global Trade Partnerships: Slovenia’s export-driven economy benefits from strong trade ties with Germany, Italy, Austria, and Croatia. Its primary exports include machinery, automotive components, and pharmaceuticals.
- Diplomatic Relations: The country maintains cordial relations with most nations, leveraging its geopolitical position to act as a bridge between Western Europe and the Balkans.
- Foreign Investment Policies: Slovenia actively promotes foreign investment through supportive policies, tax incentives, and free trade agreements.
Any Other Taxes in Slovenia
In addition to corporate and personal income taxes, businesses in Slovenia must comply with other tax obligations:
- Value-Added Tax (VAT):
- Standard rate: 22%.
- Reduced rate: 9.5% (applicable to essentials like food and books). VAT compliance involves regular filings and accurate record-keeping.
- Property Tax: Levied on property owners, with rates varying based on property type, size, and location. Commercial properties attract higher rates than residential properties.
- Municipal Taxes: Local municipalities impose taxes on business operations, such as signage fees and environmental levies.
- Payroll Taxes: Employers must contribute to social security, health insurance, and unemployment funds. The total payroll tax burden is approximately 16%–22% of an employee’s gross salary.
- Environmental Taxes: Companies in industries with environmental impact, such as manufacturing, may face additional levies to promote sustainable practices.
Social Security in Slovenia
- Healthcare: The country provides universal healthcare funded through mandatory contributions. The system offers high-quality medical services, and residents can access public healthcare at minimal costs. Supplemental private health insurance is also available.
- Pensions: The pension system ensures financial security for retirees, with contributions made during working years. Pensions are based on earnings and the duration of contributions.
- Unemployment Benefits: Workers who lose their jobs are eligible for unemployment benefits, helping them transition to new employment.
- Family and Maternity Benefits: Families receive allowances for children, maternity leave, and parental benefits, emphasizing Slovenia’s commitment to supporting families.
While Slovenia’s social security system is well-regarded, challenges like an aging population pose future sustainability concerns, prompting ongoing reforms.
Weather, Climate, and Regional Safety
Weather and Climate:
The country enjoys a varied climate, thanks to its geographical diversity:
- Alpine Region: Cold winters and mild summers dominate this mountainous area, ideal for skiing and hiking.
- Mediterranean Coast: The coastal region offers a warm Mediterranean climate, with sunny summers and mild winters.
- Pannonian Plain: This eastern region experiences hot summers and cold winters, with a continental climate.
The climate supports diverse agricultural activities and a high standard of living, with clean air and abundant natural resources.
Regional Safety and Security:
The country is one of the safest countries in the world, ranking highly on global safety indices. Its low crime rates, efficient law enforcement, and political stability create a secure environment for residents and visitors. While petty crimes like pickpocketing can occur in tourist hotspots, violent crime is rare. The country’s safety is bolstered by:
- Strong community policing.
- Well-maintained infrastructure.
- A proactive approach to disaster preparedness.
Residents enjoy a peaceful lifestyle, complemented by Slovenia’s reputation as a welcoming and inclusive society.
Passport Power of Slovenia
The Slovenian passport is one of the strongest globally, reflecting the country’s strong diplomatic and international standing. As of 2024, the Slovenian passport provides visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to over 180 countries, including:
- The Schengen Zone, allowing unrestricted travel across Europe.
- Popular destinations like the United States, Canada, Japan, and Australia.
This global mobility is a significant advantage for Slovenian citizens, fostering ease of travel for business, education, and leisure.
Scope of Education, Growth, and Opportunities in Slovenia
Education System:
The country places a high value on education, offering free and compulsory schooling for children aged 6 to 15. Its education system includes:
- Primary and Secondary Schools: Public schools provide free education, with a focus on academic excellence and holistic development.
- Higher Education: Slovenia’s universities, like the University of Ljubljana, rank among the top institutions in Europe. Higher education is affordable, with minimal tuition fees for EU citizens and moderate costs for non-EU students.
- Vocational Training: The country emphasizes skill-based education, offering programs that align with market demands.
Growth Opportunities:
- Economic Stability: The country’s growing industries, including technology, tourism, and manufacturing, offer job opportunities and career growth.
- Entrepreneurship: A supportive ecosystem, government grants, and EU market access make Slovenia an attractive destination for startups.
- Sustainability: Slovenia’s focus on green energy and environmental preservation creates opportunities in renewable energy and Eco-friendly ventures.
Lifestyle Benefits:
Residents benefit from a balanced lifestyle, with ample recreational activities in the country’s forests, lakes, and mountains. Slovenia’s emphasis on sustainability ensures clean living environments and an excellent quality of life.






