Understanding the Power Ministry’s New Scheme for Trade in Carbon Credits 2023

Understanding the Power Ministry’s New Scheme for Trade in Carbon Credits 2023
The national steering committee will oversee the market, while CERC will control trading.
In a significant move towards addressing climate change and promoting sustainable development, the Power Ministry has recently notified a scheme for trade in carbon credits. This scheme aims to incentivize industries and organizations to reduce carbon emissions and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
By establishing a market for carbon credits, the government aims to encourage emission reduction projects and facilitate the transition to a low-carbon economy.

As the nation strives to decarbonize its economy and has pledged to reduce emissions by 45% from 2005 levels by 2030, the power ministry announced the Carbon Credit Trading Scheme 2023 on Friday.
Following the plan, the Centre would create a 20–22-member national steering council (NSC), led by the secretaries of the environment and power, to oversee and coordinate the carbon market.
The Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) will oversee trading operations. At the same time, the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) will complete the steps for institutionalizing the Indian carbon market and develop the rules and regulations with the help of the NSC. The Grid Controller of India would serve as the market’s registrar.
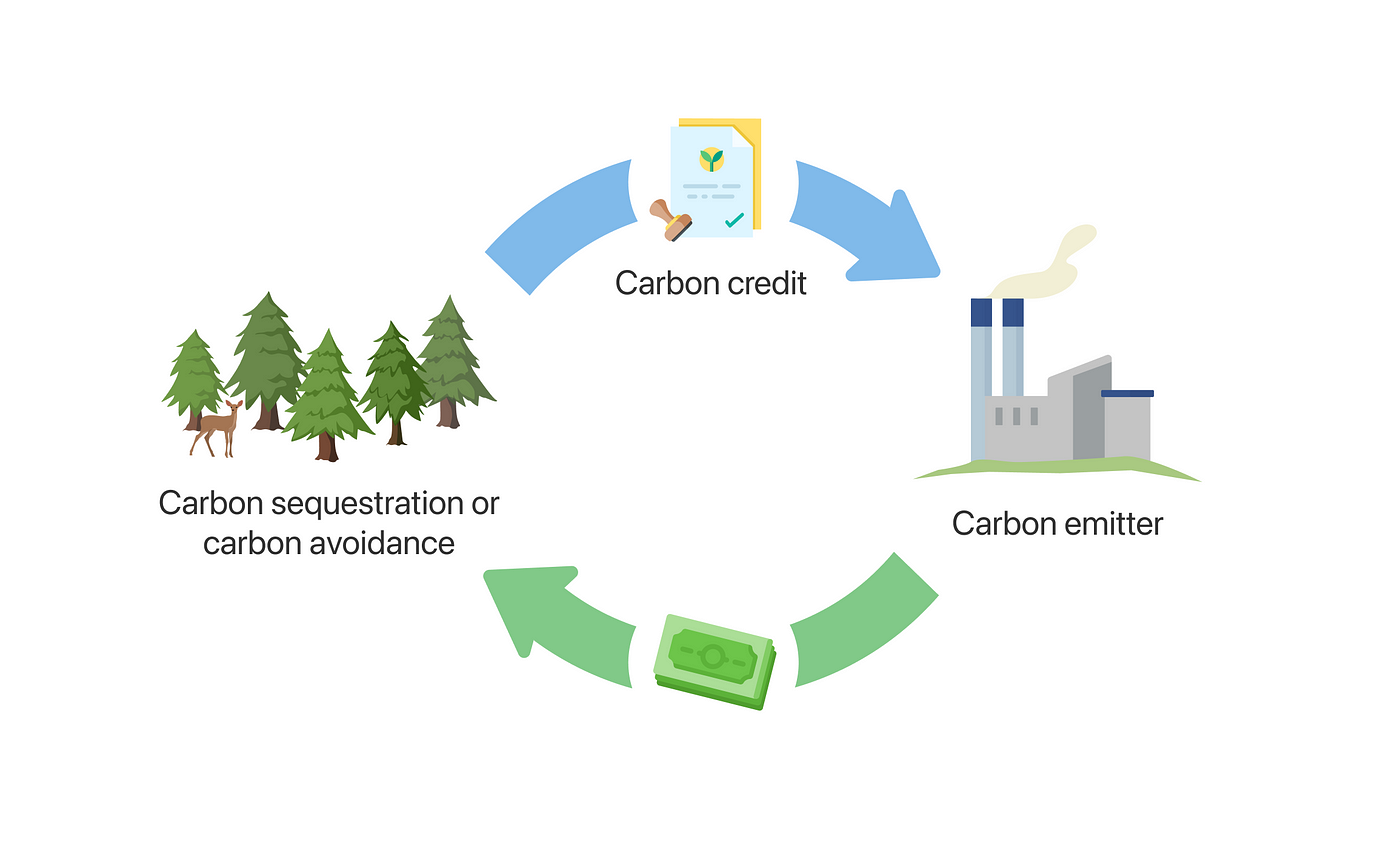
According to the programme, “Carbon credit is the value assigned to the reduction, removal, or avoidance of greenhouse gas emissions achieved and is equivalent to one tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent (tCO2e).”

The BEE will select the sectors, set emission reduction goals, issue certificates for carbon credits, and certify the organizations that verify carbon emissions.
Carbon credit certificates will be granted if the required entities achieve more significant emission reduction than their predetermined objective. The certificates from the carbon market will be purchased by entities that fall short of their goal.
Understanding Carbon Credits:
Carbon credits are tradable certificates representing reducing or removing one metric ton of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) emissions. They are generated by projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions beyond what the law requires. These projects range from renewable energy installations to efficiency improvements or reforestation initiatives. By creating a monetary value for carbon reductions, carbon credits incentivise businesses and organizations to invest in sustainable practices and technologies.
Key Features of the Scheme:
The scheme notified by the Power Ministry lays the foundation for a robust carbon credit trading system in India. Here are some of its key features:
- Eligibility and Verification: Industries, power plants, and other organizations successfully reducing their greenhouse gas emissions can participate in the scheme. Accredited third-party entities must verify the emissions reductions to ensure transparency and credibility.
- Issuance of Carbon Credits: Upon verification, eligible projects will receive carbon credits corresponding to their emissions reductions. Each credit represents one metric ton of CO2e reduced or removed from the atmosphere.
- Trading Platform: A dedicated trading platform will be established to facilitate the buying and selling carbon credits. This platform will bring together buyers and sellers, allowing them to trade credits at market-based prices.
- Compliance and Voluntary Markets: The scheme allows compliance and participation. Compliance market participants, including power plants and heavy industries, will be mandated to offset a certain percentage of their emissions by purchasing carbon credits. Voluntary market participants, such as businesses and organizations committed to sustainability, can voluntarily participate in the scheme and offset their emissions.
- Price Discovery Mechanism: The trading platform will facilitate price discovery through transparent and efficient mechanisms. The balance between supply and demand in the market will ultimately decide. the price of carbon credits, incentivizing emission reduction projects and providing economic benefits to sellers.

Implications and Potential Impact:
The notification of the scheme for trade in carbon credits carries several implications and potential impacts:
- Environmental Benefits: The scheme incentivizes emission reduction projects, promoting cleaner technologies and sustainable practices. Encouraging industries and organizations to adopt greener alternatives Contributing to reducing greenhouse gas emissions will help combat climate change.
- Economic Opportunities: Establishing a carbon credit trading system creates new economic opportunities. It creates a market where carbon reductions can be monetized, providing financial incentives for sustainable investments and facilitating the growth of clean energy and technology sectors.
- International Cooperation: By aligning with global efforts to combat climate change, India’s scheme for carbon credit trading enhances its position in international climate negotiations. It demonstrates the country’s commitment to reducing emissions and contributes to the global transition towards a low-carbon economy.
- Social Responsibility: The scheme encourages corporate social responsibility by motivating businesses to take concrete steps towards sustainability. It allows organizations to showcase their environmental commitment, enhancing their brand value and reputation.

The Power Ministry’s notification of the scheme for trade in carbon credits marks a significant step towards sustainable development in India. By creating a market for carbon reductions, the system incentivizes emission reduction projects, promotes the adoption of cleaner technologies, and contributes to global efforts in mitigating climate change. Establishing a carbon credit trading system presents economic opportunities and demonstrates India’s commitment to sustainable growth. As businesses and organizations embrace the scheme, they contribute to a greener future and position themselves as responsible stewards of the environment.




