Official statistics: 140 convicts at Ghaziabad’s Dasna Jail have been HIV-positive.
Official statistics: 140 convicts at Ghaziabad’s Dasna Jail have been HIV-positive.
Ghaziabad: On Friday, a top jail official announced that 140 detainees at the Dasna district jail in Ghaziabad had received HIV diagnoses. Before being admitted to the prison, all inmates are subjected to an HIV test per government regulations.

According to Alok Kumar Singh, superintendent of the district jail, the convicts at the Ghaziabad Jail are examined by medical professionals from the antiretroviral therapy center housed in the MMG district government hospital.
The State National Aids Society organized HIV testing clinics in jails in 2016. In the Ghaziabad Prison, 49 inmates were discovered to have HIV at the time. Following that, the government mandated that all new detainees have HIV and TB testing as part of a general health checkup. Just at Integrated Counselling & Medication Centre (ICTC) inside the jail, if an inmate is found to have HIV, ARV treatment is given to them.
The Ghaziabad jail now has almost 5,500 convicts incarcerated despite having a maximum of 1,706 inmates. “Of the 5,500 prisoners, 140 are HIV positive & 35 are also TB positive. Since 2016, there have been 120 to 150 HIV-positive inmates residing in prison on average, according to Singh.

Following that, the government mandated that all new detainees have HIV and TB testing as part of a general health checkup. At the Integrated Counseling and Medication Centre (ICTC) inside the jail, if an inmate is found to have HIV, ARV treatment is given to them.
Following that, the government mandated that all new detainees have HIV and TB testing as part of a routine health checkup. There at Integrated Counselling and Medication Centre (ICTC) inside the jail, if an inmate is found to have HIV, ARV treatment is given to him or her.
Describe HIV.

A particular kind of chimpanzee in Central Africa is where humans first contracted HIV. According to studies, the human-chimpanzee transmission of HIV may have begun as early as the 1800s. The virus that affects chimpanzees is known as the simian immunodeficiency virus. When people killed these chimpanzees for food and came into contact with their sick blood, it was likely transmitted to humans.
Over many years, HIV gradually spread throughout Africa and then to other regions of the world. Since then, at least in the mid-to-late 1970s, the virus has been present in the US.
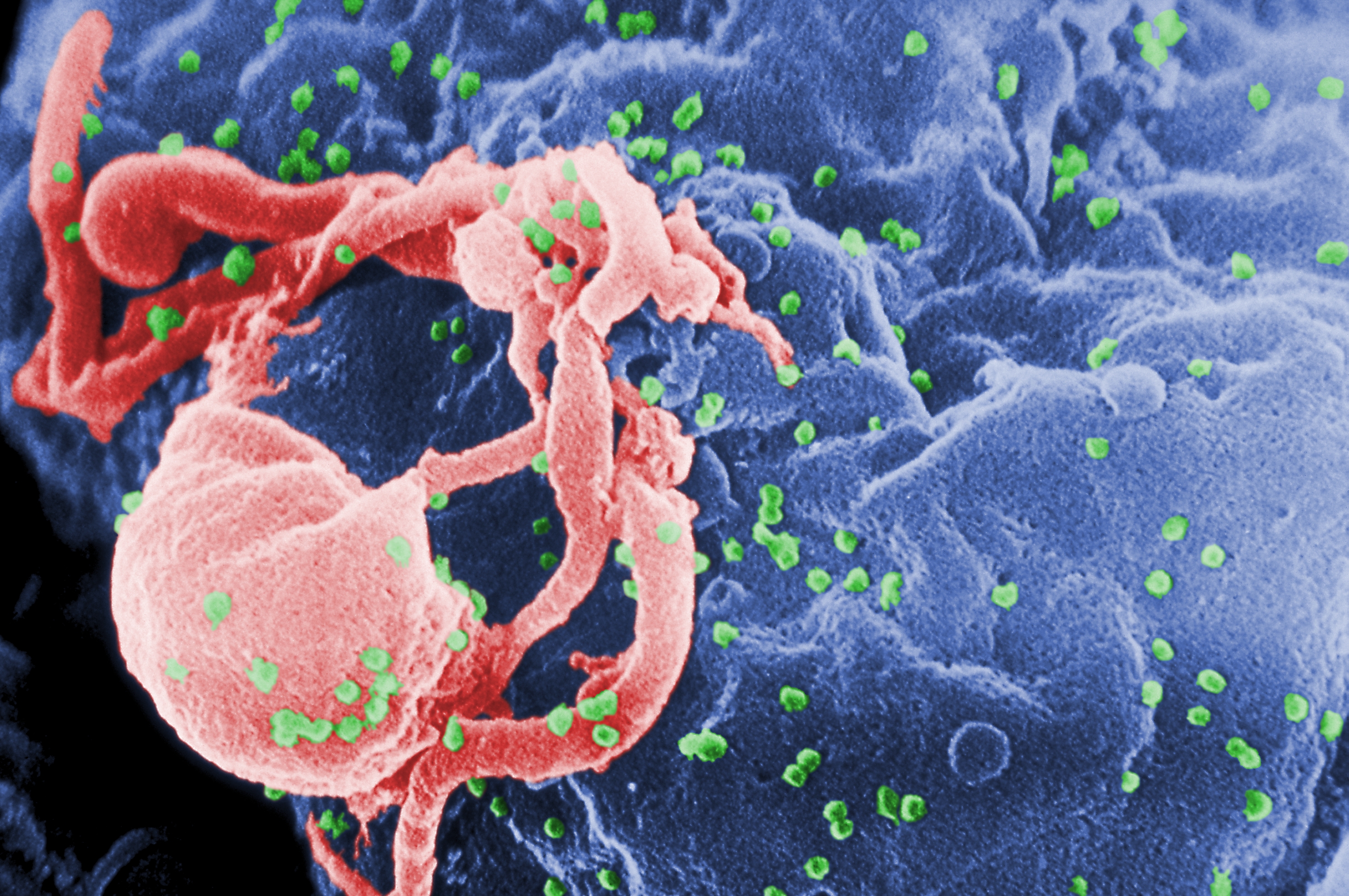
Immunodeficiency virus, sometimes known as HIV, is a persistent, potentially fatal viral infection that weakens the immune system and impairs your body’s capacity to fight against illness and disease.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-590279757-9b886dbd225a485fb8d2e1a2c09ca484.jpg)
There are three significant ways HIV can spread: through intercourse, contact with contaminated blood, and drug use that involves illicit injections or sharing needles. Additionally, it can be passed from mother to kid while she is pregnant, giving birth, or nursing. Without treatment, it can take years for HIV to progressively impair your body’s immune system, and you develop AIDS.
Despite the fact that there is no treatment for HIV/AIDS, medical professionals claim that drugs and lifestyle adjustments can control and stop the disease’s progression.
Numerous antiviral therapies have been developed throughout the years, which have decreased the number of AIDS-related fatalities globally. According to the WHO, it hopes to reduce the number of Hiv cases from 1.5 million by 2021 to 335 000 by 2030, as well as the number of fatalities from 680 000 in 2020 to under 240 000 in 2030.
Symptoms and signs

Before the virus fully explodes into AIDS, the indications of HIV can be noticed in several phases. According to medical professionals, some people experience symptoms similar to the regular flu at least four weeks after contracting the virus. The virus spreads quickly, despite the fact that the disease may only last a few days. HIV can only be identified through a blood test. Despite the majority of symptoms being so minor, you would hardly detect them.
Several of the signs include:
Excessive body aches and pains in the muscles and joints; a high fever; recurring headaches and migraines; rashes and itchy food intolerances all over the body; a sore throat; mouth sores and ulcers; swollen lymph nodes; diarrhea; and nausea. Unexplained weight loss; frequent colds and coughs; and night sweats.
Having HIV/AIDS
Living with HIV is not particularly challenging, and the effects of the virus may be managed with sound therapy, according to medical professionals. You will be urged to do the following things as well:
- Consume a nutritious, balanced diet
- Give up smoking
- Get vaccinated against the flu each year to lower your risk of contracting severe illnesses
Without therapy, the immune will suffer significant damage, and potentially fatal conditions like cancer and severe infections can develop.
edited and proofread by nikita sharma




