Top 10 Best Deep Tech Companies in India 2023

Top 10 Best Deep Tech Companies in India 2023
The phrase “deep tech” distinguishes it from its opposing concept, “shallow tech.” A business can transition from a non-digital to a digital business model using shallow technology, a relatively important technological advancement. Shallow technological advancements are simple for rivals to copy. Thus they don’t usually cause as much market disruption.

Swati Chaturvedi, the CEO and Founder of the online investment product Propel(x), which connects early-stage Deep Tech with investors, is credited with coining the term “deep tech.” Deep-tech startups are those whose business models are built on significant scientific advancements or high-tech technical innovations.
Shallow technology could include, for instance, a once-telephone-based delivery service that is now provided digitally through a phone app or a bookstore that now provides e-books for digital download.
Although Uber fundamentally disrupted the taxi industry, it is not considered deep technology because it established a platform employing already existing, widely-available digital technologies on top of the sharing economy.
When it comes to deep tech, the industry revolves around genuinely revolutionary technology. It is used to tackle practically impossible issues in the actual world. Artificial intelligence, deep learning, or other increasing application to new or existing technological innovations are expected to be the foundation of deep tech firms.

Like blockchain, digital imagery, and virtual reality, Deep technology examples could be artificial intelligence used to forecast natural disasters or genetic imaging techniques that can detect disease or a tendency to disease much earlier than any other test.
What Makes Deep Tech So Unique?
Artificial intelligence (AI), clean energy, life sciences, agribusiness, aerospace, chemistry, and industry are the key fields in which deep tech startups are active. Deep tech rarely resides in a single sector by itself. Because it’s a game-changer by nature, there are aeronautical technologies utilized to monitor agricultural conditions, an advancement in artificial intelligence used to produce sustainable energy, or a patient being monitored.

Deep technology differs from deep tech and other startup types in a few ways. Deep tech businesses typically have a board of advisers that includes CTOs rather than CEOs because the technology powers the entire company. They frequently hold patents or other intellectual property, and they often tested the technology for years in a lab or some different research setting before attempting to bring it to market.
Deep tech companies may require significant long-term investments and major amounts of research. Since we’re talking about disruptive innovations that might take longer to get market adoption fully, commercial success could likewise take longer.
Where Is It Going?

Deep tech sectors like artificial intelligence (AI), composite technologies, blockchain, biotech, robotics, drones, photonics, and quantum computing are developing from early research to commercial applications at an ever-increasing rate. It resembles a new industrial revolution in that new platform technology and infrastructures drastically alter our daily lives and workplaces.
Suppose you consider how much the world has changed since the last wave of emerging platform technologies, like the the internet, mobile devices, personal computers, and microchips. In that case, you can start to see how deep technology could advance different industries and help solve or lessen issues like global warming, illness, feeding a growing world population, and dealing with aging populations.
The test and prototype phases are now easier to access and move through more quickly than ever because of innovations like 3D printing, Gene sequencing, and computer-aided design. So, the faster these key technology platforms reach the market, the greater the prospects for them.
1. Instoried
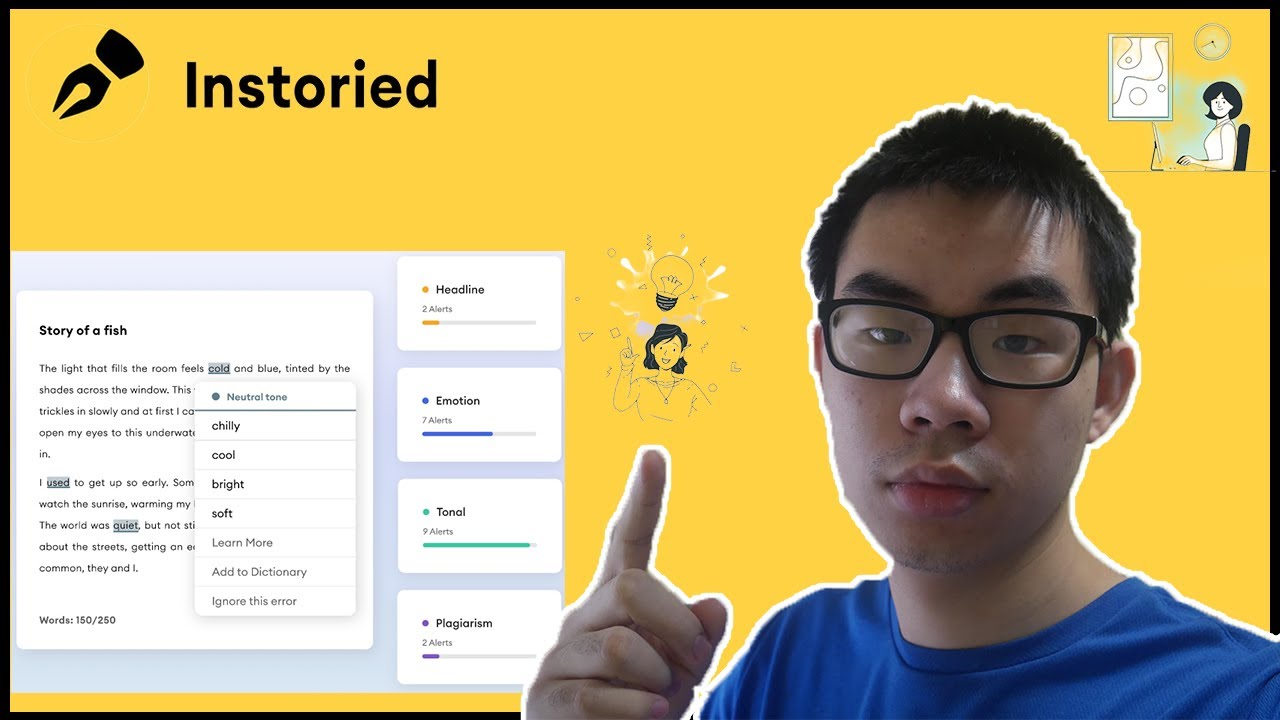
Web platform Instoried, with offices in California & Bengaluru, recently inked a contract with GEM International Yield, an alternate investment company located in Paris, New York, and, indeed, the Bahamas. Following the agreement, GEM will provide a Share Subscription Facilities of up to $200 million that the firm may use for 36 months after becoming public. Additionally, it received $8 m in Series A fundraising in October 2021 from investors, including Mumbai Angels, SOSV, Innovative Catalysts Angels Fund, Pritt Create Mutual, and 9 Unicorns.
The depth startup stated that it intended to use the funding to increase its international marketing efforts, especially in the United States, and reinvest in its technology to expand its product line with a Chrome Browser extension, a WordPress connector, and other features.
With the money, Instoried plans to improve its AI-based content creation platform, broaden its reach internationally, and strengthen its executive team. The business intends to IPO traditionally or through SPAC.
2. Deep Vision

Deep Vision, a deep tech business with offices in Hyderabad and California, raised $35 million in a Series B fundraising in September 2021 under the leadership of Tiger Global Management. Exfinity Vc, SiliconMotion, & Western Digital were in the Series A investors who took part in the crowded round.
The business has raised around $54 million in capital to date. Accordi ng to Deep Vision, the funds will be used to increase the functionality of its AI processor, software tools, and product development. They will beused to ramp up hardware production and serve the company’s quickly expanding customer base. In 2014, Wajahat Qadeer, Rehan Hameed, and Ravi Annavajjhala founded Deep Vision, a company that creates processors for AI used to develop.
The company focuses on use cases for camera-based technologies in retail, EV and driver monitoring, innovative city projects, drones, and automation systems.
3. AgNext

AgNext Technologies, an agricultural technology business based in Chandigarh, raised $21 million in a Series A round of funding in August 2021. The game was led by Alpha Wave Incubation (AWI), with involvement from previous investors Omnivore and Kalaari Capital. According to a statement from the business, the capital round gave a-IDEA, an agribusiness incubator conducted by the National Academy of Agricultural Management (NAARM), a 5X exit.
Seed funding for AgNext, formed in 2016, came from a-IDEA. The deep tech startup stated that it intended to use the funds raised to expand into fresh commodities and markets abroad, including those in the Mid East, Europe, and South Asia.
The money will be utilized to create Qualix, its technology platform, allowing for quality-driven trading activities across the food supply chains. Additionally, it intends to open a new headquarters in Abu Dhabi.
Next, a company created in 2016 by Taranjeet Singh Bhamra uses its patented technology to address the issue of quality analysis. Through the use of its full-stack “Qualix” platform, it provides quick food quality evaluation using a combination of AI, ML, Internet – Of – things (IoT), plus advanced data analysis. The startup’s physical and chemical examination solutions cover a wide range of commodities, such as grains, spice, tea, milk, and even animal feed. Clients include ITC, Bajaj, NAFED, Verka, and others.
4. Strartforge

A deep tech firm based in Gurugram raised $7 million in its most recent fundraising round, which Accel organized. Other notable investors, such as Storm Ventures, Smile Group, Decathlon Ventures, Core91, and well-known founders and CXOs from top online firms, participated in the round. The business stated it would put the additional funds into hiring staff, accelerate international expansion into the US marketplace, and establish a cutting-edge computer vision center for more in-depth space research and development. Additionally, it plans to broaden its technological perspective to include AR/VR to develop goods for Metaverse or Omniverse.
To assist huge eCommerce markets in the automobile, fashion, and retail industries and increase the visual value of the photographs without a physical studio, the AI tech firm claims to produce 100 percent autonomous, industry-first AI image analysis products. With its solutions, businesses can create studio-quality photographs 500 times faster and grow their operations instantly.
The company claims it presently provides services to over 80 customers in 15 countries, including Amazon.in Flipkart, Karvi, OLACars, SellAnyCar, and Udaan. The business recently introduced Stratforge AI Cars, a self-serve AI solution for the automobile sector. It will replicate this model for the e-commerce and food sectors in the following months.
5. Astrodome

Astrodome, a Deeptech firm with offices in Bengaluru and California, raised $million in bridging financing in September 2021 that was co-led by IAN Fund, Urania Ventures (Germany), and Cognizant founder Lakshmi Narayanan. Along with a group of US-based angel investors, other investors in the round included Impact Collective (South Korea), ArtPark (India), and others. The business had previously received funding from the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, and several angel investors.
The funds raised will be used for US market expansion, bolstering operator trials worldwide, and advancing its critical technologies’ commercialization through new products. Dr. Neha Satak and Dr. Prasad H. L. Bhat founded Astrodome in 2015 to provide Gigabit speed communication services to telecom providers, businesses, and the military.
Its unique telecom radio and satellite communication products aim to hasten the deployment of 5G in suburban regions and broadband in rural areas. The firm wants to make E-band a competitive fiber substitute. Its GigaMesh multi-beam E-band product is a transmitter that can wirelessly link base stations or cell towers to the leading network.
The product is used in three industries: last-mile rural, urban telecom, and defense communications. With the Indian Defense Forces, the firm entered into a deal to implement GigaMesh to meet the nation’s needs for strategic communication. It inked its first international contract with a South-East Asian cellular provider in 2021.
The startup further asserted that it was the first company in the world to be chosen by Qualcomm and Verizon’s 5G accelerator program, EvoNexus, in San Diego, Ca. Astrodome is currently developing the 50 Gbps per unit GigaMesh-Next E-band radio. Appropriate for the construction of 5G networks in the future. In addition, it plans to put GigaSat, a Flat Screen Satellite (FPS) interface, into operation in the upcoming years. It will assist in meeting the demand for affordable user terminals that LEO satellite broadband providers have.
6. Genrobotics

Bandicoot is a spider-shaped robotic that cleans sewage and is created by the Kerala-based startup Genrobotics to replace the cruel practice of human labor someday. The solid and liquid waste that clogs urban sewers is scooped up by a 50 kg pneumatically propelled remote-controlled robot that descends into a maintenance hole and spreads its extensible limbs like a spider. It has a robotic arm with a 360-degree motion that can brush the maintenance hole’s floor and collect dirt in a bucket, cleaning the maintenance hole covers in 20 minutes.
Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, and Gujarat have all adopted Bandicoot. Engineers Vimal Govind MK, Arun George, Nikhil NP, and Rashid Abdulla Khan founded Genrobotics in 2015. Bandicoot employs machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) to calculate how much unclogging is necessary and can do the task in 45 minutes. In contrast, manual labor would take three to four hours.
Genrobotics also makes the Manhole Surveillance System (MMS). MMS is a comprehensive sanitation solution that monitors the maintenance hole network. It gathers the necessary data and uses computer vision and AI technology to analyze it to give a general assessment of the sewer’s health and inform users when it becomes clogged or overflows.
Genrobotics makes the 10-foot-tall G-Robotic Suit, a robot that a person may control by putting himself inside. It is a working prototype of a technology that might be applied to weightlifting, space travel, and other uses that call for more strength and security.
7. Cogknit

An innovative product company with ISO certification based in Bangalore is called Cogknit Semantics Pvt. Ltd. It uses machine learning in computer vision, speech, and text. The business’s Nimit platform, which uses machine learning and data science systems to determine users’ learning strategies and user behavior to identify users’ context and produce information according to the context, allows them to obtain an extended melded learning platform.
Congknit believes they can take advantage of the vocal style transactions that will upend different industries. It runs a lot of video material in its stores and strives to ensure that even a consumer with visual impairments can follow the scripts.
Semantics, Web 3.0, Big Data, systems analysis, and related technologies are the center of the startup’s expertise and innovation as they address diverse industry issues.
8. Cognitifai

Kanishka Nithin developed the company Cognitifai, which employs a video analytics platform and computer vision to catalog physical world occurrences to let users recover precise information through cameras. They have developed expertise in urban monitoring, including surveillance, healthcare, and the discovery of hyper-local intelligence for innovative urban and retail businesses.
In contrast to relying on a human store employee to inspect and restock the stock, Cognitifai can recognize even one bottle from the store’s inventory using its computer vision technology. This allows the store to replenish the shelf considerably more quickly.
Consequently, real-time intervention is made possible to aid in inventory management.
Cognitive founded the following products:
- Visionapi.ai is an online marketplace for cutting-edge visual clues use cases and techniques that make it simple for various organizations to find, access, and application use cases and scenarios. Instead of investigating, concentrate on finding a solution to your company’s problem.
- DevSuite.ai is a collection of user-friendly, no-code visual modeling tools that covers the entire lifecycle of developing an Ai system or AI product from production.
- HPCOS.ai is an os for training, inferencing, and life-long learning of AI at a scale that is entirely managed in a highly distributed and parallel environment. All are independent of the location and process of running AI. Consequently, your time to produce AI at scale will be reduced from months to minutes.
- Dataplatform.ai is a platform for the safe distribution, management, and processing of massive data sets from big sources.
9. Nautilus
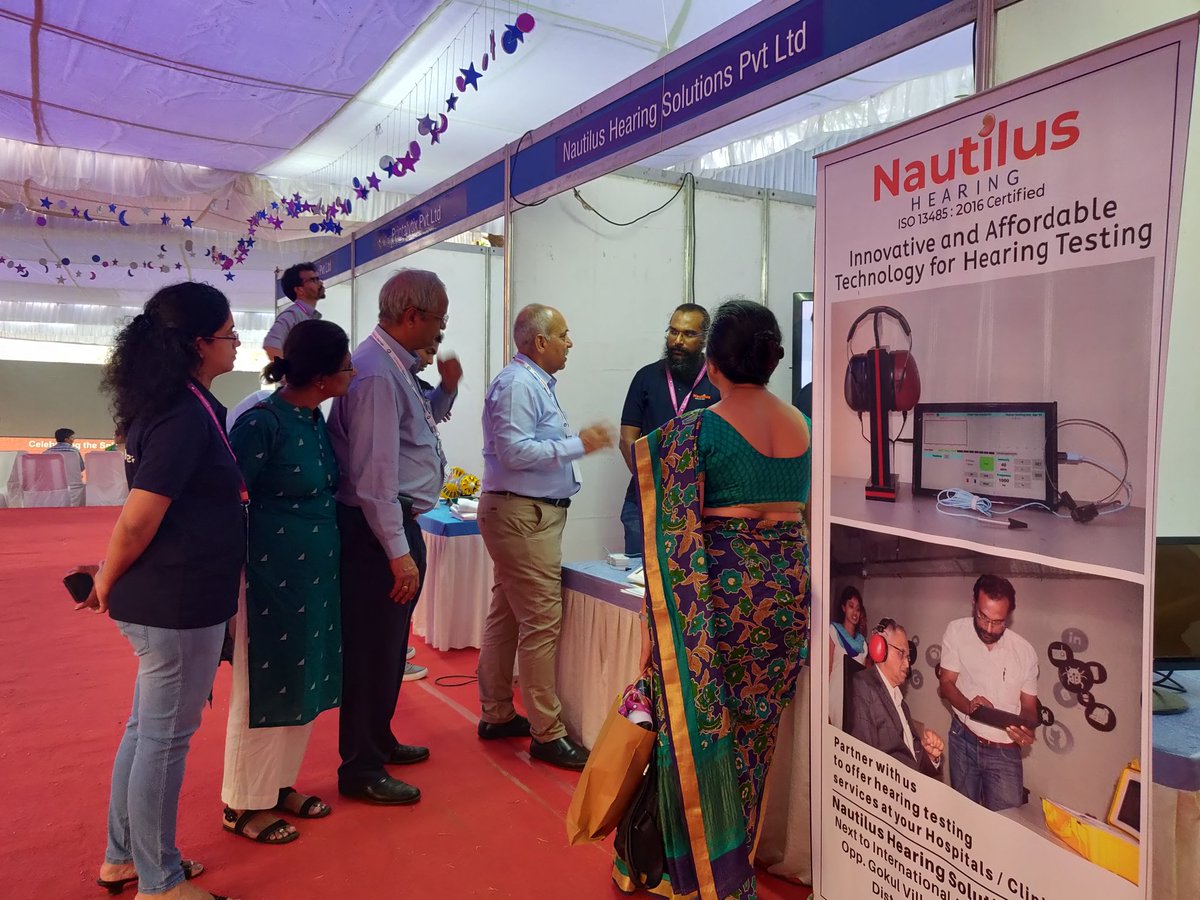

Nautilus Audiologist T. Uday Raga Kiran founded the accessible and cost-effective firm Hearing Health Care. By using cutting-edge technology that creates new opportunities in audiometric testing, the startup creates a new kind of auditory care company goods that are simple, accessible, and dependable.
People frequently only wear their cochlear implants for brief periods before stopping when they no longer find them comfortable. The business has created a portable, booth-free audiometer that makes it simple for doctors to do ear exams. Two versions of Nautilus Hearing are available.
A diagnostic tool for licensed healthcare professionals and a screening tool for use in loud-equipment-using industries, institutions, schools, and NPOs. By winning the Karnataka Government’s ELEVATE 100 Program, Nautilus Hearing raised an undisclosed amount of money. Clinical studies will shortly begin after the startup has finished its early testing. The team put the apparatus to the test at an All India Institute of Hearing and Speech in Mysore.
10. Streamoid

Nvidia, Manthani, Rajesh Kumar, and Haricharan Lakshman created the artificial intelligence stylist company Streamoid in 2014. To provide trendy, relevant, and tailored results for fashion shopping, Streamoid Technologies employs its expertise in picture recognition to extract product and style data from pictures and process it through an AI engine.
The clothing and retail sectors are the startup’s primary industries. Streamoid comprehends the user’s fashion query’s natural language, photos, voice, and context. Users can interact with it similarly to a highly knowledgeable sales associate in the fashion industry. The fashion and apparel industries are flourishing more than ever. Therefore Streamoid is sure to become well-known shortly.
You receive your own custom-designed, created, hosted, and managed style bot from Streamoid. You may help your consumers with tailored style suggestions using Streamoid’s conversational interface.
Thanks to advanced NLP and integration, style bots have many benefits over human agents. Style bots are available 24/7, can respond immediately to many conversations, provide individualized help, and save money.
Top five deep technology use cases
Many industries stand to gain from deep technology’s enabling qualities. Here, we’ve chosen to concentrate on the most critical topics.
1. Life Sciences
The Boston Consulting Firm estimates that in 2020, 51% of deep technology companies will be focused on the health sector. Precision medicine has already achieved major progress due to the rapid development of healthcare custom software, allowing technologists and researchers to collect precise health-based data and create novel, individualized treatments.
Deep tech is used in this industry for things like AI diagnosis, sensors for tracking and diagnosing health, digital health records that let medical professionals tailor treatments, and online appointments.
2. Processing and computerization

Since the invention of the computer, its basic design has not changed much. Today’s computing requirements are all met by the same machine, whether for online grocery shopping or deciphering massive databases. Computers can be specifically designed using deep technology to address particular issues or challenges.
The proliferation of other cutting-edge technology, like computer vision, which has its own computation and processing requirements, has made quantum computing one example of how profound tech could increase computing and processing capabilities. Additionally, the energy requirements of the current computer infrastructure render it unsustainable over time.
3. Agri-food technology
One of the main problems facing humanity today is food insecurity. Deep tech solutions that can help us transition away from the industrial era’s traditional farming practices and toward more environmentally friendly production techniques are thus desperately needed. Using cutting-edge innovations like big data, blockchain, and biotech, cutting-edge startups in the food and agriculture sector are creating interconnected farming methods with highly accurate forecasting capabilities that allow farmers to grow and extract their crops for maximum efficiency, resilience, and yield.

Another area being researched is synthetic biology, which The Business Research Company estimates will generate $27 billion in revenue by 2023. With it, it is believed that we will be able to hasten the natural systems’ rapid evolution and the development of new, more stable forms.
4. Cleantech and energy
Deep tech businesses are employing energy software engineering and cutting-edge technology to research hydropower generation or, for example, to increase the efficiency of solar and wind power with the Web of Things. The energy industry needs to undergo a fundamental transition. The major barrier to renewable energy right now is storage. Several creative companies are working to overcome it by developing batteries and maximizing their use using cloud-based technology.
5. Infrastructure
Governments must create the infrastructure needed to support the growing population. This has sewage systems, housing, power plants, supplies, and other infrastructure. However, those same governments are coming under major pressure to cut carbon emissions and support long-term solutions to population increase.
Furthermore, global epidemics like COVID-19 will occur more frequently as we expand deeper into natural areas, according to the most recent G20 insights. This means that whatever we construct going forward must be created with consideration for the environment, utilizing sustainable manufacturing techniques, and promoting an improved standard of living for people. Urban planners and cutting-edge technologists must work together heavily on this and make a major financial investment.
edited and proofread by nikita sharma




