Artificial Intelligence (AI), cloud computing, 5G, and Nanotech in healthcare: How organizations are preparing best for the future

Artificial Intelligence (AI), cloud computing, 5G, and Nanotech in healthcare: How organizations are preparing best for the future
Automation, digitalization, and technological enablement are having a significant impact on several industries. The healthcare industry is not an exception. The healthcare delivery system in India is changing and is about to advance significantly. The pandemic has shown that healthcare organizations can become innovative, flexible, and resilient by utilizing tech-enabled business models that place data at the core.
Additionally, healthcare organizations quickly realize that no matter how technically advanced their services or products are, they will no longer be applicable. To produce not just an enhanced product or service but also a better healthcare experience, it is imperative to connect with users along the healthcare value chain, be they patients or physicians. Fortunately, technological progress has accelerated the process of change required for Indian healthcare to become digitally linked and shown promise for enhancing people’s healthcare experiences.
Advancements in Healthcare Creating the Future’s Roadmap

India has already begun developing a national digital framework to create a digital health ecosystem on a national scale. The market for digital healthcare in India was estimated to be worth INR 116.61 billion in 2018 and is projected to reach INR 485.43 billion by 2024, growing at a CAGR of 27.41 per cent. Adopting electronic health records for the whole population is one of the several steps made in that regard.
Healthcare organizations are quickly embracing innovative technology to change how care is delivered in the nation and benefit the healthcare ecosystem as a solution to address the problems that the country’s healthcare system is now facing. Here are a few new technologies that are changing things:
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and digital representations of the human body’s physiology make it possible to anticipate the chance that chronic diseases will advance based on the decisions being made. By using these simulations, healthcare professionals can better comprehend options and therapies and their consequences on patient health outcomes and influence on related expenditures.
Additionally, AI is helping healthcare professionals manage illnesses holistically, better coordinate care plans, and help patients manage and adhere to their treatment regimens. Further, statistics indicate that administrative expenses account for 30% of healthcare expenditures. The bulk of these duties, such as keeping track of bills that need to be paid and maintaining records, may be automated with AI, considerably cutting expenses.
Cloud Computing
The collaboration between physicians, nurses, and departments has grown crucial as healthcare organizations throughout the nation transition to value-based care. Thanks to cloud computing, accessing patient information has gone from a sluggish and laborious procedure to a quick and easy process.
With cloud computing, data may be stored centrally and made accessible from any location at any time. In addition, cloud infrastructure allows users to adjust health data storage depending on the new patient volume. IoT-enabled devices are being offered to patients by a variety of healthcare providers. By connecting these devices to a healthcare provider’s cloud system, patient data may be swiftly delivered to the doctor. This makes for a quicker diagnosis and better treatment.
The 5G Network
Every aspect of healthcare has the potential to be improved by a 5G connection, particularly since the healthcare sector is still recovering from the ravages of the epidemic. Large data files and real-time, high-definition video may be transmitted over a fast network to handle telemedicine appointments. Patients may reach medical professionals more quickly and receive treatment more quickly thanks to the use of 5G, especially in remote places.
Nanotech
Utilizing nanotechnology has given the healthcare sector new opportunities. Researchers and scientists use this technology to improve medical imaging, target tumours, and medication delivery systems. Additionally, the technique reduces costs, speeds up DNA sequencing, and provides scaffolding for tissue regeneration or wound healing. Further, artery obstructions are being removed by nanobots or micro-scale robots, as are quick biopsies of worrisome cancerous tumours.
Major Healthcare Technology Trends of 2022

The healthcare sector is anticipated to strengthen in 2022, thanks to groundbreaking discoveries and technologies. Most of the significant modifications are still in the future!
This article will examine the main medical technology developments and changes anticipated for the medical industry shortly.
The focus is often on lowering the cost, increasing access to healthcare services, and identifying and treating problems sooner rather than later. The US healthcare industry is expanding quickly; by 2026, the national healthcare product’s value is predicted to reach USD 6 trillion. It’s never too late to prepare for the many available healthcare possibilities. Make sure to use digital technology to increase revenue, and staff productivity, achieve better financial results, and improve patient care.
- New AI Applications and Medical Community Concerns
Artificial intelligence (AI) technology has advanced quickly in recent years, and this trend will persist in 2022. Among the various sectors that gain from AI, medicine mainly uses it for accurate illness diagnosis and detection, albeit this is not the only use. IBM Watson, for instance, is one of the AI systems already accessible for use in business and healthcare.
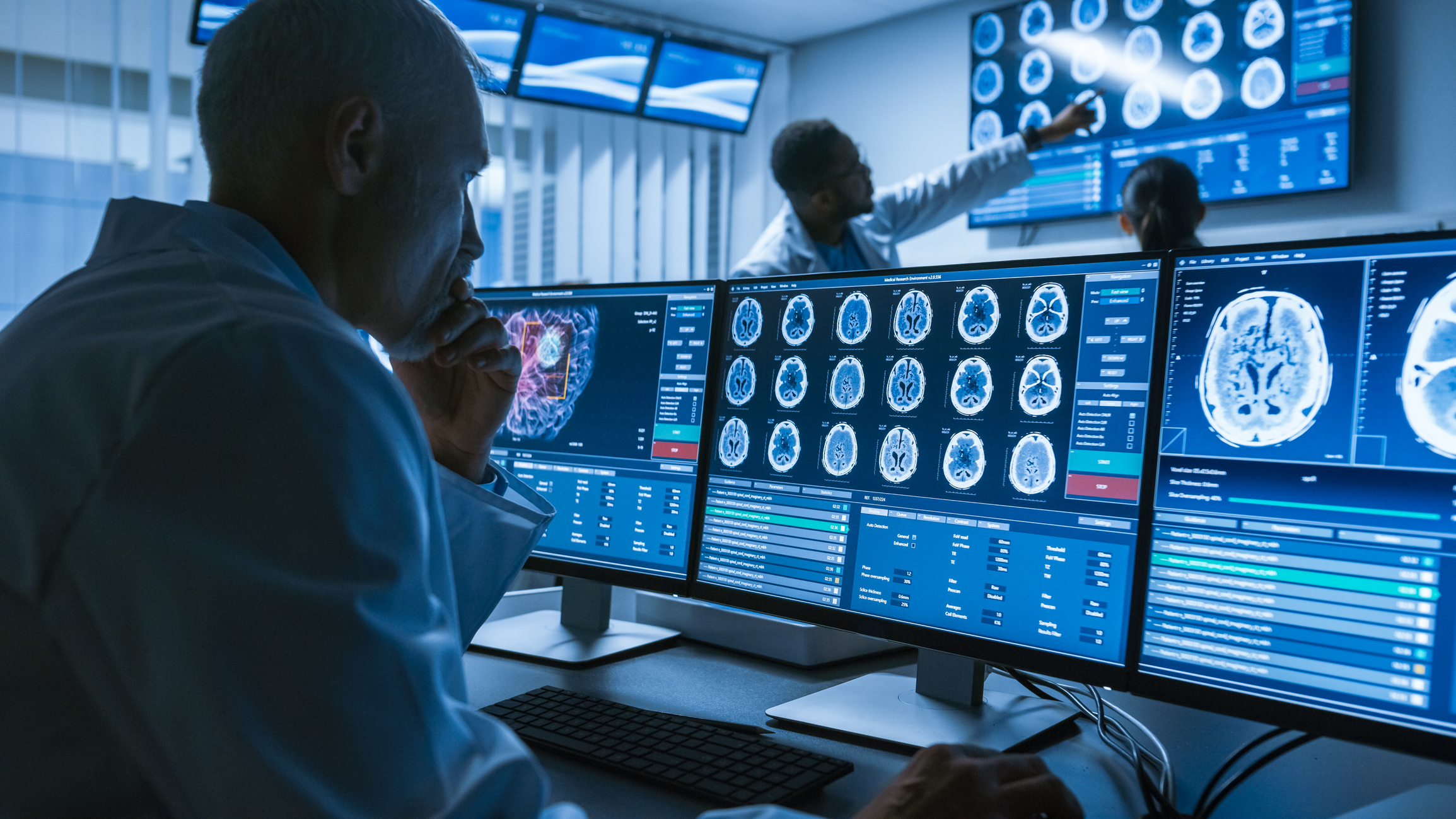
Computed Tomography Scan Analysis
The demand for computed diagnostic professionals (radiologists) has significantly grown since the COVID-19 epidemic struck the world’s population.
AI-powered technology could provide a solution. AI systems can quickly evaluate CT images from hundreds of patients, identifying pneumonia patterns brought on by COVID-19 and informing physicians of these. That would make up for the lack of qualified labour in this industry.
Before our eyes, innovative ideas are taking shape. For instance, a deep learning model for imaging COVID-19 was developed to recognize COVID-19 patterns in CT images automatically. The Microsoft-sponsored InnerEye research project is another promising endeavour for processing computed tomography scans. Even though accuracy has significantly increased, radiologists are still hesitant to entrust the digital mind with crucial choices. AI cannot be held responsible for a poor diagnosis or ineffective course of therapy. Instead, the expert who decided to employ AI must pay for their error and take every precaution to limit the adverse effects while maximizing this digital health trend.
Because of this, most cutting-edge clinics employ AI as an additional tool rather than a stand-alone diagnostic or therapeutic method. It is excellent for validating current diagnoses or enhancing research data that has been gathered conventionally.
Machine Learning in Biopharma and Medtech
The pharmaceutical sector will effectively capitalize on technological advancements in healthcare by utilizing AI to discover new medications. A group of British and Japanese scientists filed a patent for the first medicinal molecule created by AI in January 2020. The drug will be used to treat obsessive-compulsive disorder after it passes muster for testing on humans.
AI-enhanced lab research has also led to the discovery of other intriguing formulations since late 2021, including some potential treatments for uncommon and extremely severe ailments. Numerous cutting-edge studies, such as molecular modelling and simulation of chemical reactions in multi-factor settings, leverage AI and machine learning approaches to support chemical experiments and therapeutic medication development.
Since many tests may be carried out electronically, this method enables scientists to reduce the number of expensive onsite experiments using reagents and high-tech lab equipment. It also hastens the discovery of critical scientific innovations.
Automating Hospital Workflows using Robotics
Startups from all over the world will pour hundreds of millions of dollars into creating AI projects in 2022, including various forms of robotic systems, which may enable them to reduce the cost of recruiting trained medical personnel. The intention is to assist medical facilities that already have a severe shortage of nurses and clinicians as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has put the entire healthcare system under unprecedented strain, rather than to replace people with machines, which would lead to unemployment and a decline in social standards. Learn more about creating medical HR software to assist HR professionals in addressing the U.S. medical workforce problem.
Innovative enterprises should keep in mind the medical community’s restrictions on AI-driven software, its capabilities, and its applications as they work to realize these lofty goals. Modern medicine has countless applications for robotic assistance and automated systems, including cleanliness, surgery, remote diagnostics, etc. However, the healthcare system’s top goals will always be the well-being of medical personnel and the effective treatment of patients.
In light of this, robotic and AI-driven technologies will be employed to support current procedures rather than replace them, resulting in a potent fusion of the present and the future. Daring projects combined with sound regulation are a prominent trend in the digital health sector. It will enable physicians to utilize cutting-edge technology fully, learn to apply it in satisfying and secure ways, and steer clear of any pitfalls.

Symptom Checker Chatbots
Chatbots are computer programs with artificial intelligence (AI) support (often not true AI but powerful algorithms) that engage in meaningful conversations that resemble those between humans using voice, text, or option-based input.
Every area, including healthcare and medical consultancy, is seeing a rise in their use. These solutions, available around-the-clock online or via mobile devices, can provide preliminary medical diagnoses and health advice based on input and complaints from a patient. Chatbots can also be connected with unique patient portals for hospitals and clinics. When human medical assistants are unavailable, they can assist patients with their health issues and worries, even in acute situations (such as disaster-induced overloads of call centres, peak or non-operation hours, etc.)
These chatbots can aid patients in determining their subsequent actions and motivate them to seek professional medical advice when necessary. Care must be exercised, though, since it may result in inaccurate self-diagnosis and disinformation.
Globalization of AI Requirements in Healthcare
Ten recommendations that can serve as the foundation for the creation of GMLP have been developed by a powerful coalition of the U.S. FDA, Health Canada, and the United Kingdom’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) (Good Machine Learning Practice). These guidelines will help programmers and AI engineers create secure medical equipment, software, and systems powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) components. This shows that governments take the potential and hazards posed by AI exceptionally seriously and would want to regulate the use of AI in healthcare practices as soon as feasible.
Adoption of AI-backed Technologies
The main drawback of the advancement in artificial intelligence technology is that hackers will use it to target medical systems and steal secured healthcare information, rather than only to save human lives or help medical personnel with their everyday responsibilities. One of the growing dangers to the security of medical technology in 2022 and beyond is sophisticated malware with AI capabilities.
Which medical technology solutions are in jeopardy? Almost everything could have weak security or security flaws, such as wireless systems in hospitals, clinics, or health centres, EMR/EHR solutions, IoT, and computer-aided healthcare provider and health insurance company systems. Intricate phishing and social engineering assaults can also target clients and staff members.
Hackers may use this feature to simulate personal identities as part of next-generation super-personalized social engineering and phishing campaigns, which have the potential to be as dangerous and deceptive as ever before due to AI’s growing capacity to mimic photorealistic 3D faces or organically sounding voices. This necessitates installing high-end data protection methods that can mitigate any hazards by hacker techniques aided by AI.

- Data Breach Prevention
Despite all the technological safeguards and healthcare providers’ knowledge, statistics on data breaches show a sharp rise over the previous ten years, with infractions peaking in 2020–2021. These data breaches impact thousands of patients around the US. Hopefully, healthcare organizations will focus more on data security and their digital ecosystems in 2022. Healthcare cybersecurity is quickly emerging as a popular technological topic this decade.
How to Prevent Data Breaches in Healthcare?
The security of medical records, which is governed by HIPAA and EDI in the healthcare industry, is a top priority for the US government.
Every healthcare professional should follow a few effective procedures:
- Conduct yearly cybersecurity audits to ensure that everything follows HIPAA security regulations and high technological standards.
- Outsourcing projects or ongoing tech maintenance only works with responsible third parties.
- Maintain training and education for your medical personnel on data security and cybersecurity concepts, risks, best practices, and adverse effects of non-compliance.
- Maintain expert tech oversight over your devices and medical records by having staff log off unused devices and schedule regular anti-malware scans, among other precautions.
- Ensure that all systems are current and secure against unwanted access.
- Manage your facility’s Wi-Fi network to prevent unauthorized users from accessing any password-protected sections.
- Manage your IT infrastructure to guarantee all devices’ safety and proper operation.
- Employ a capable internal IT manager.
Facial Recognition With Masks
Face recognition technology, which permits approved access for medical professionals to mobile devices or workstations, rose to popularity due to its ease.
Deep learning facial recognition algorithms must be used in the COVID-19 pandemic to distinguish staff members wearing masks. Specific sources claim that some businesses have already achieved 99.9% accuracy in the face recognition of people wearing masks.
- Nanomedicine
Nanotechnology may still seem like science fiction, yet it is steadily influencing our daily lives. By the end of 2021, fantastic news about the creation of tiny, organic robots that can reproduce themselves will reach every part of the globe. Therefore, it is realistic to anticipate that 2022 will bring forth several significant advancements in the nanomedicine sector. Early investments are welcome in the burgeoning nanomedicine industry.
Here is a brief explanation of what nanomedicine is: it uses nanoscale (microscopically small) materials and objects, like biocompatible nanoparticles, nanoelectronic devices, or even nanorobots, for specific medical uses and manipulations, like the diagnosis or treatment of living organisms. The injection of a group of nanorobots into a human’s blood vessels might be utilized as a possible hunter for cancer cells or viruses, for instance. This method is anticipated to effectively combat a wide range of cancers, rheumatoid arthritis, and other hereditary, oncologic, or auto-immune illnesses on a cellular level (or even become an ultimate solution to them).
- Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
Even though the IoMT will not be a novel concept by 2022, this industry will experience exponential growth. Every one of the several digital health developments in this sector has excellent applications for healthcare professionals and has the potential to save billions of dollars.
- Mobile apps and Wearables in Healthcare
Apps for remote health monitoring and wellness will continue to grow in popularity in 2022. You may discover a decent number of professional (and many other semi-professionals) mobile applications for healthcare and health in the GooglePlay or iTunes libraries.
Some mobile applications can connect to wearables like pulsometers or fitness trackers to use the information gathered by the sensors attached to your body to report or evaluate your health problems, including blood pressure, body temperature, pulse, and other metrics.
- Intelligent, autonomous medical devices
Autonomous nursing robots or self-moving smart gadgets can substantially assist by minimizing the tasks linked to supply management or sanitary maintenance that medical professionals must perform.
Different types of robots can work in various hospital-based settings and jobs, protecting human workers from infection risks or stress from the extreme burden imposed on many US hospitals by a COVID-19 patient overflow. An Italian hospital, for instance, employed robot nurses during a COVID-19 severe epidemic. These clever assistants were utilized to remotely check patients’ blood pressure and oxygen saturation levels because they are two critical indicators of their present state of health. Those levels might decline quickly, necessitating emergency intervention for the patient. This drastically decreased the requirement for nurses to visit patients in person.
- Social Determinants of Health Gain Value
Healthcare systems primarily concentrate on elements within their area of expertise: quality and price of medical services while generating risk assessments and accumulating illness data. However, they represent the very beginning. Before patients feel symptoms and seek the help of physicians, a host of other less apparent circumstances impact them.
Initial health problems are caused by factors other than a lack of care. Their origins are deeper; they are found in social, environmental, and demographic contexts that are rarely taken into account in the context of conventional clinical diagnoses.
Medical institutions mainly handle symptoms and offer advice on lifestyle modifications, having a minimally significant influence on treatment results (between 10% and 20%). In addition, between 80% and 90% of health outcomes are determined by non-medical variables. The term “social determinants of health” refers to these elements (SDOH).
In 2022, healthcare providers will approach SDOH with greater caution than ever before and carefully review patients’ medical histories, taking into account details that were overlooked in earlier years.
Doctors will shift from treating symptoms to prediction and prevention based on patients’ SDOH predisposition to particular diseases to stop the advancement of dangerous health concerns and reduce individual medical expenditures.
- Smart Implants
More implant-related options and technology will hit the global and American healthcare markets in 2022. This offers dramatically improved regenerative medicine effectiveness, patient rehabilitation, and a solution for many disabilities previously thought to be incurable.

Increasing the Use of 3D Bioprinting
By 2027, it is anticipated that the medical industry’s volume of 3D printing potential will surpass $6 billion. Even if 3D printing biocompatible implants is not a novel technique in 2022, new materials and more advanced prosthetic methods will make this technology more dependable and available to a more extensive range of patients. In particular, it is anticipated that advancements in 3D bioprinting technology would improve the following areas:
- Reduce the time and cost of manufacturing implants and bionic prosthetics.
- More reasonably priced personalized bionic knee, spine, skull, and hip replacements.
- Medical equipment and surgical tools can be designed specifically for a patient.
- New implant technologies, types, and materials are intended to function, fit better, and endure longer.
- Mechanical limbs that can operate fully, more lightweight prosthetic designs, and higher levels of bone-implant integration.
- More choices for 3D-printable, life-saving implants for those with neurological and cardiovascular conditions.
Neural Implants
In 2022, effective options for brain-computer implants are anticipated to debut. Neuralink plans to begin inserting its devices into human brains at least in 2022. More businesses, groups, initiatives, and startups are preparing to market their neuro-implants for various medical requirements, including regaining functional independence in patients with multiple forms of paralysis or blindness.
For instance, it was stated that by the end of 2021, a team of scientists had implanted a microelectrode array (a penny-sized implant) into the visual brain of a blind individual, enabling her to recognize several letters and shapes. Although there is still a long way to go, brain implants’ potential to help people with various disabilities seems to have a genuinely fantastic and promising future.
- Integration of Big Data and Data Silos with Healthcare Systems
Healthcare businesses will employ an exponentially growing number of data sources, and the volume of gathered healthcare data (including patient records, DICOM files, and medical IoT solutions) will also rapidly increase. Medical service providers will seek contemporary platforms, such as data fabrics, to combine and handle massive amounts of dispersed and structured data.
It will be among the tasks to build safe multi-cloud solutions capable of transporting significant amounts of data to manage, store, and mine it for valuable insights and to link siloed data with the healthcare systems.
- Payer-Provider Bonds Will Strengthen the Patient’s Benefit
Healthcare payers and providers frequently have interests that clash. The standard of their collaborative work decreases when both sides take absolutist positions. Patients, therefore, do not get the care they need. They are frequently mistreated, have to wait longer, and pay more.
Both payers and providers should embrace a value-oriented mindset and work toward group goals rather than individual success. All parties must understand that they are working for the same purpose—providing high-end healthcare to the public—and that if either suffers losses, the other will no longer support them. All organizations involved in the healthcare sector will hopefully try their utmost to learn how to collaborate in 2021. They will concentrate on delivering complete care, move from settling disagreements to cooperation, and communicate information to support successful decision-making.
- Widespread Use of Telehealth
The healthcare sector is already seeing the effects of the vast diversity, universality, and growth of digital communication channels. A brand-new channel for distributing medical data is telehealth. It entails delivering healthcare services remotely through the Internet, videoconferencing, streaming services, and other communication technologies. Long-distance education for patients and medical professionals is included in telehealth. Telehealth has achieved widespread acceptance and has evolved into a regular procedure in 2021. Modern clinics already counsel their patients electronically. This kind of communication will replace conventional internal dialogues and receive full regulatory permission in the upcoming years.
- By 2022, China plans to implement telehealth in 70% of its public hospitals, thanks to a national initiative.
- The US is a pioneer in telemedicine. To lower the cost of healthcare services by reducing the upkeep expenses of medical facilities, the government wants to develop additional off-site solutions in the following years.
- Other developed nations also focus on telehealth and creating their programs while considering regional demands and unique characteristics.
With the introduction of 5G wireless, telehealth will expand rapidly and be universally adopted shortly.
- Overcoming Mental Health Challenges with Telepsychiatry
In 2022, a wide range of elements will impact mental health and pose new difficulties for medical practitioners. Telepsychiatry, a relatively emerging speciality in psychiatry and mental health care, has been stimulated by COVID-related restrictions.
The COVID-19 outbreak is causing psychological destruction among many people, as evidenced by clinical statistics. According to recent data (October 2021), over 30% of American adults report anxiety or depressive disorder symptoms, whereas earlier surveys suggested that the same indicator was less than 10% in 2019. This branch of medicine has a broad horizon for development.
In 2022, the following common mental health phenomena will have an impact on the mental health of Americans:
- psychological problems associated with going back to the office (or hybrid workstyles).
- Post-covid syndrome includes signs of a mental illness.
- Health care workers who have had PTSD.
- Anxiety and despair are brought on by COVID’s effects on social restrictions and lockdown procedures.
- Digital overload, the stress of multitasking, and burnout in the workplace.
Modern solutions are needed to address these new problems, such as behavioural health software that enables psychiatrists and psychotherapists to assist more patients concurrently.

- More Digital Health Unicorns Will Exit via IPO
Most often, ambitious and receptive companies bring cutting-edge innovations to the field of medicine. Large businesses with established workflows seldom pursue novel innovations.
These small firms must develop something remarkable and valuable to stand out from the competition. Most of them concentrate on digital innovation. Those who successfully increase their wealth to $1 billion or more are called “digital health unicorns,” a word that defines an uncommon and exceptional organization.
The choice to sell the project or its shares comes naturally after a startup’s management can stand firm on its own two feet and access sufficient authority and resources. Before mergers and acquisitions, most digital health unicorns were sold through mergers and acquisitions. However, in 2019 there was a surge in IPO activity. More and more startups prefer this exit strategy. This may be explained by the monopolistic risks associated with mergers and acquisitions, as major healthcare providers swallow up smaller businesses to gain market domination and ultimate control.
Numerous healthcare unicorns that went public in the US, UK, Germany, China, and other nations in 2019-2020 have a combined value of more than $70 billion. In 2021, experts anticipated that even more outstanding startups would IPO their shares.
- Preventing disease with big data and analytics
Technological advancement is unrelenting, and the amount of healthcare data that has been amassed recently is astounding. Scientists can find new connections between demography, environment, economy, and many other aspects on the one hand, and health issues of the population on the other, using the enormous arrays of data anonymized for this purpose.
When scientists have access to enough data, they can process it as Big Data. Big Data can then be put into AI or machine-learning algorithms to be evaluated and interpreted and provide humanity access to previously unattainable medical discoveries. These analytics offer chances for long-term treatment planning and the avoidance of chronic diseases. Big data may also aid in preventing pandemics, such as the intelligent concept of using analytics to combat COVID-19.
You don’t need data from millions of patients to draw valuable inferences. An electronic health record (EHR) system is the most widely used piece of healthcare software that enables data collection and analytics.

- Support for gene therapy projects will be provided by annuity reimbursement
Gene therapy is a rapidly developing field of study and medicine. Using the human genetic code, clinicians can cure various disorders without medications or surgery by introducing specific genes into a patient’s body.
However, this market segment is still in the testing phase. Investors’ worries about the expensive cost of research and equipment, hazy pricing models and administrative processes, a shortage of patients, and a lack of thorough safety and efficiency data have resulted in a severe need for reimbursement. Reimbursement is currently only offered in Germany and Italy. An annuity-based strategy is far more successful than reinsurance, dynamic pricing, or formulae based on outcomes and income. These choices are characterized by a lack of effective oversight and the involvement of several insurers, which results in confusion and disarray.
According to experts, the widespread adoption of an annuity-based reimbursement model will give gene therapy initiatives the secure financial foundation they need to pay for research and the use of cutting-edge technologies and assist them in generating revenues of over $2 billion in 2021.
- Data sharing and interoperability among healthcare entities
Every clinic typically maintains a database containing information on all of its patients. This method requires patients to undergo thorough diagnostics each time they seek a new healthcare professional, resulting in double spending on recurrent treatments.
To achieve interoperability, a shared database that can be accessed by all clinics that provide care for a particular patient must be created. Given the interdependence of the systems in the human body, a complete medical picture can lead to significantly better outcomes than a narrow collection of information that only includes a few reported symptoms but not the underlying causes of health problems.
With solid support from the government and investors, 2022 takes interoperability initiatives to the next level. Healthcare systems that operate alone and refuse to exchange data with other organizations will become obsolete and less influential.
- US government officials push healthcare providers to change their enterprise-centred practices to patient-centred ones and to share patient information.
- The European Union is implementing cross-border interoperability and improved data protection.
- Interoperability will be adopted by developing nations in Asia and Africa as part of broader eHealth policies intended to improve access to and management of medical data in such countries.
For the development and expansion of open systems, cutting-edge software technologies like platform integration and APIs will be leveraged. By the decade’s end, the medical sector will use blockchain to store patient health records.
- Challenge with Legacy Healthcare Software
In their process, healthcare institutions may use old (also known as a legacy) software systems.
In spite of this, legacy software systems should not be used. Medical records may be subject to several dangers, including the chance that patient data may be compromised, computer glitches, incompatibility with current software platforms and modules, system interference, or brute-force hacking. The most recent HIPAA regulations should be considered while evaluating older software solutions.

- Consumerism in the Medical Market
More than ever, the medical sector resembles a market for goods and services. Healthcare organizations that compete with them use marketing techniques to offer customers (patients) services. Many providers are willing to meet their requirements when a patient wants a particular medical service. The only businesses that will succeed in the long term in their fields are those that comprehend their customers and adjust to their complex needs.
In 2021, the consumerism tendency in healthcare will intensify. Medical goods and services will be sold digitally through marketplaces and online shops. Customers may acquire information, compare it, and schedule medical services online with a few clicks.
Pharmaceuticals and medical supplies made by well-known companies are available on websites like Walmart and Amazon.com. In 2021, there will be an increase in businesses operating online, offering detailed information about their costs and utilizing e-pharmacy, telehealth, and retail care.
- Precision Medicine Will Displace One-Size-Fits-All Treatment
Precision medicine considers a patient’s genetics, way of life, and surroundings to ensure the accuracy of their diagnoses and the effectiveness of their treatments. The one-size-fits-all approach ignores a wide variety of unique features and is based on the characteristics of an average patient. To efficiently collect and evaluate patients’ actual data and provide precise diagnoses and therapeutic recommendations, state-of-the-art informatics facilities and technologies are required.
By 2022, it is anticipated that cutting-edge initiatives will start to take shape in this market, raising its value to $5 billion and bringing the healthcare sector one step closer to the widespread adoption of precision medicine. Emerging precision informatics technologies will benefit providers, payers, pharmaceutical companies, and other interested parties while being safe and compatible. To meet the demands of diverse businesses and their clientele, they will put numerous diagnostic patterns to use.
- Wider Deployment of PULSE
A digital platform called PULSE (Patient Unified Lookup System for Emergencies) gives healthcare volunteers access to the medical records needed to treat patients effectively in crisis and catastrophe situations. This approach, introduced in 2018, has already shown effectiveness, so we can anticipate its wider rollout in more regions in 2022.
Final Words

A significant change is about to occur in the Indian healthcare sector due to the quick digitalization of services and goods. While the Center is making great strides to encourage the rise of digitization in healthcare, further changes are needed to open up every potential path for growth in the sector.





