Government Introduced New Geospatial Sector Policy: What Is The New Geospatial Data Policy? Why Is India Liberalizing Its Geospatial Sector? Why Is It Important?

The Union Ministry of Science and Technology issued a new policy for the country’s geospatial sector on Monday. This move is significant because the government has decided to liberalize geospatial data and geospatial data services.
It also decided to delete the existing agreement in this regard. This will make the geospatial field a more competitive field.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi stated that this will be a key step towards the realization of the “Atmanirbhar Bharat” vision, adding that this move will help the country’s public sector, private sector, start-ups, farmers, and researchers.
What Is The New Geospatial Data Policy And Why Is It Important?
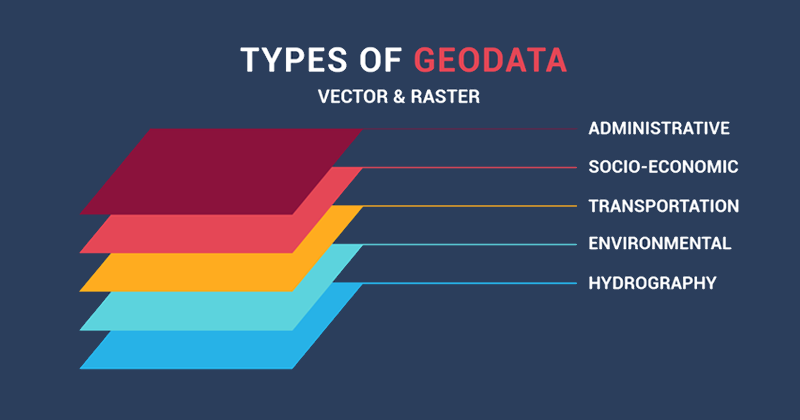
Geospatial Data
Geospatial data is all data representing objects on the surface of natural or artificial earth. Geospatial data can be static (such as road locations) or dynamic (such as a moving vehicle).
These data are also the precise coordinates of objects or events on the surface of the earth and the attributes of the objects or events, and sometimes even the combination of the time or life span of these locations and attributes.
How Can Geospatial Data Help And Useful To Common People?
Geospatial data is very important because it can provide people with information about the location of roads, water bodies, facilities, locations, and railway lines.
Over the years, the use of geospatial data by ordinary people has greatly increased because it forms the background of the entire Google Maps or any other such applications, and they also form the basis of navigation features.
However, it is not limited to this. Due to geospatial data and geospatial data services, real-time delivery of food can also be tracked on Swiggy or Zomato, or real-time location can be tracked on WhatsApp or Ola.
Current Geospatial Policy
So far, decades of geospatial policies have not been reviewed. Therefore, companies and innovators have been strictly restricted to obtain prior approval and pass other strict procedures and the resulting red-tapism before they could collect, generate, prepare, publish, disseminate and update digital geospatial data and maps in India.
This means that India’s geospatial sector is mainly controlled by several central agencies such as the Union Government and the survey of India.
Since this policy has not been reviewed for decades, in accordance with the prescribed guidelines, the collection of geospatial data is done only for security reasons, so it can only be under the control of the government and the National Defense Forces.
Any private company that wants to create such data must obtain permission from the relevant department and obtain approval from the Union Ministry of Defense and the Home Ministries.
What Does The New Geospatial Data Policy Say?
While sharing detailed information about the new policy on geospatial data and related services, Dr. Harsh Vardhan, Union Minister of Science and Technology, said that publicly available geospatial services make previously restricted geospatial data more versatile, thereby making certain previous restrictions and the guidelines are outdated.
With this new policy, Indian entities will not need to obtain prior approvals, permits, or security clearances to obtain and generate such data and related services, including maps.
In addition to this, according to the new policy, the government has decided to provide all geospatial data collected with public funds to all Indian entities for economic, development, and scientific purposes, unless the data has been collected for classification purposes for security or confidentiality purposes law enforcement agencies.

Why Is India Liberalizing The Geospatial Sector?
India is rapidly moving towards infrastructure development, which has become a necessary condition for the same level as other countries in the world.
Through initiatives such as smart cities and digitalization in India, advanced systems such as urban public transportation, delivery and logistics, and global technological advancement to launch products such as e-commerce, automated drones, etc., geospatial data is important to undertake mapping to ensure appropriate development.
However, India is riddled with a lack of data. With the resolution and accuracy required to perform this task, if the government sets out to complete this task on its own, it may take a long time to complete.
By opening up the sector, the government will not only allow more people to complete this difficult task but may also rely on the competitiveness of the private sector to complete this work faster. Quick mapping is the need of the hour’s work, so follow-up work can be carried out faster.
Not only that, the process of approving the use of such data by private entities is a time-consuming process that unnecessarily tying up both government and private sector resources.
Now, private-sector entities will be able to self-certify and comply with the guidelines without the government having to consider their every move, thus making private entities more independent and freeing up government resources.
The government expects that with this policy, the private sector will be able to bring innovations in the sector and generate more solutions based on this, which will lead to an increase in employment in the geospatial sector and also promote economic growth.
In addition to this, the government hopes that, with the opening of such data, it will also witness the improvement of the efficiency of agriculture and related departments.




